Obesity: What You Should Know and Some New Research on the Condition

Key Takeaways
It’s safe to say that obesity is one of the most pressing public health issues right now. But when did it become a public health crisis, and what is the prevalence of obesity today? It depends where you look. According to research, The National Institutes of Health declared obesity a disease in 1998. The American Obesity Society announced it as one in 2008, and The American Medical Association voted to recognize it as a disease in 2013.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), obesity is an epidemic in the U.S. As the CDC notes, over one-third of adults in the U.S. are obese, with the number continuing to rise—more than two in five adults has obesity! And as data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found, in the U.S. alone, one in every 11 American adults has severe obesity.
The WHO also found that worldwide obesity has tripled since 1975. So, with the rates of obesity on the rise, now’s as good a time as any to explore some of the new research being done on the public health issue. After all, we need new, innovative strategies to address the disease. But first, what actually is obesity?
What Is Obesity?
When most people hear the word “obesity,” they probably think of someone very fat or overweight. But obesity is about more than weight gain, and obese people are not just "fat."
Instead, obesity is a medical condition that can arise from and lead to many health problems, and people with obesity suffer from several health risks. The disease is a public health issue because of these health risks and the healthcare costs associated with them.
Obese adults are not just overweight; they also have excessive body fat that can cause medical issues. The health problems associated with it include high cholesterol, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease. It is also one of the leading causes of death in the United States and is associated with other health risks like diabetes, stroke, and certain cancers. Obesity may also lead to mental health issues due to its effects on quality of life.
How Is Obesity Diagnosed?

Did you know that there are different ways to diagnose obesity? It’s not just a matter of stepping on the scale to track weight gain. Doctors use other measures to determine whether someone has excessive body fat. An official diagnosis can be important information for people struggling with obesity who are trying to reach a healthy weight as they may need to go about it in a specific way, depending on the results.
To diagnose obesity, your doctor will first ask you about your medical history and family history. They will also ask you about your current lifestyle and eating habits. Your doctor will then perform a physical exam, which may include measuring your waist circumference and body mass index (BMI).
BMI is the most common way to diagnose obesity. Still, it is not always the most accurate as it does not consider any increases in muscle mass. Still, obesity, defined as BMI, looks something like this:
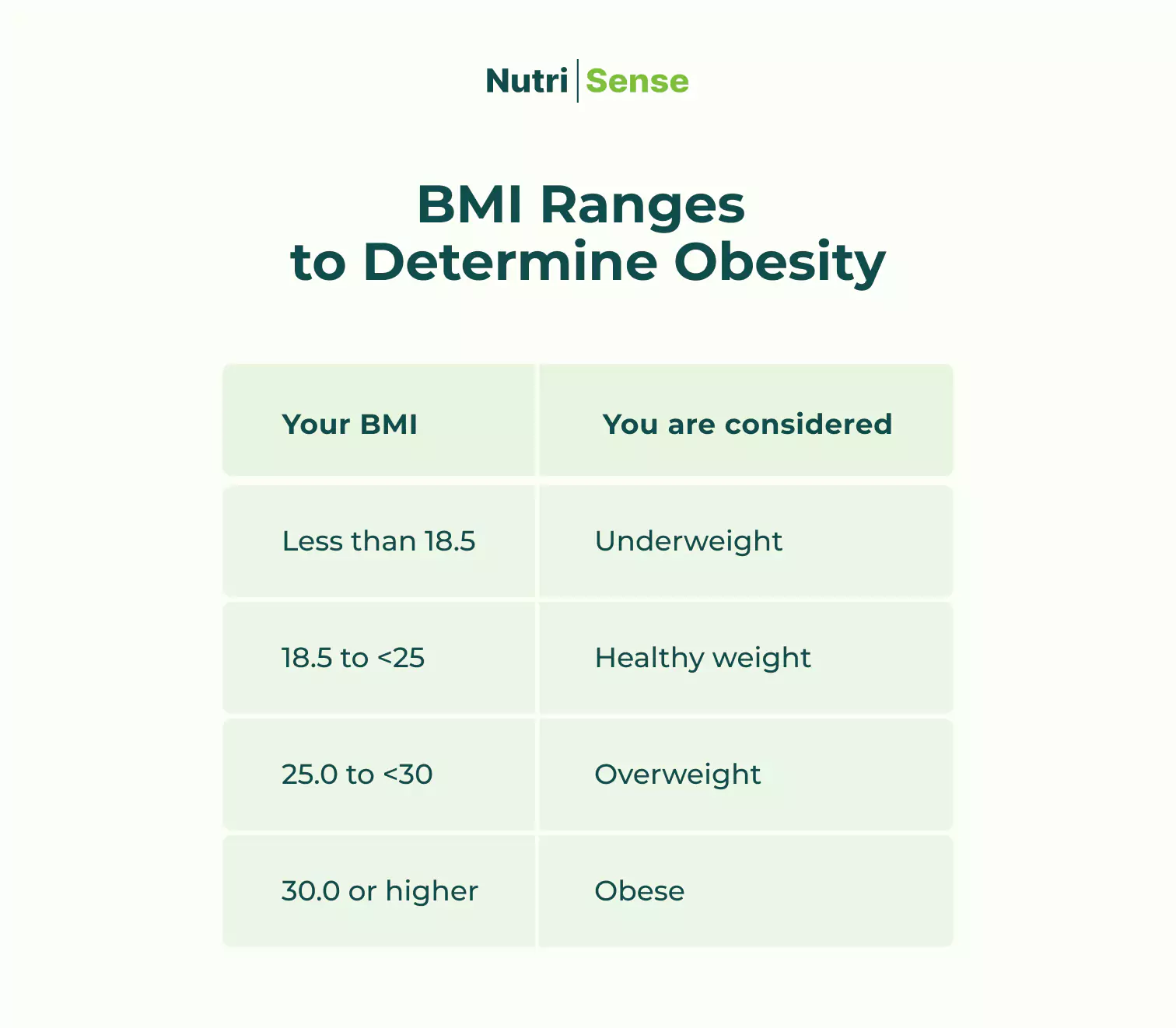
Another (perhaps better) way to measure obesity may be with waist circumference measurements of >40 for men and >35 for women. If your healthcare provider believes you are obese, they may order blood tests or imaging scans to determine the cause of your obesity.
What Is the Most Recent Research on Obesity?

In the past, some outdated approaches saw too many calories and a lack of physical activity as the leading causes (sometimes the sole causes) of obesity. And while these are contributors to the issue, there’s more to it than that.
Researchers are constantly seeking new information on the causes and potential solutions for obesity. The most recent research on obesity looks at various reasons for the rise in the prevalence of obesity, including environmental and lifestyle factors. Here’s just a few you should know about:
Genetic Factors
One of the most recent studies is from January of 2022. Conducted by researchers at Penn State, it links genetic information that can help doctors identify risks for obesity in young children.
Other studies are looking at the possibility that a large part of the problem with obesity isn’t just excess weight. It may be the fat that is no longer being used to store energy, leading to a loss in functionality.
Metabolomics
Research has begun on the effect of using metabolomics. Metabolomics is the study of the biochemical products and substrates of metabolism, which are influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. Studying these compounds gives us insight into underlying biochemical activity and the state of cells, tissues, and organs.
Fitness Levels

While the idea that the prevalence of obesity is solely due to a lack of physical activity is outdated, it’s not wholly unimportant. Physical activity is a crucial part of preventing or reversing obesity. Inactivity is linked to several health issues and can significantly increase your risk of various diseases and conditions, including diabetes, hypertension, and obesity.
Covid19
Speaking of quarantines, data gathered since the outbreak of the Covid19 virus shows that obesity was linked to a higher rate of ICU admission. Obesity is also a source of morbidity and mortality. Some research found it may lead to a higher risk of needing mechanical ventilators as your body fights off the virus.
Psychological Factors
A study conducted in 2019 interviewed participants about their current psychological states and eating habits and examined their physical condition. It found that not only is obesity linked to psychologically induced emotional eating, but also with lower socioeconomic status.
Flavonoid Treatments
Some research seems to suggest that flavonoids, which are phytochemicals found in plants and plant-based foods, may help treat obesity. But the majority of research examining the link between phytochemicals such as flavonoids and obesity is still somewhat limited and to draw stronger conclusions about the connections here, more research is needed.
The Role of Genetics
There is a great deal of debate within the scientific community surrounding the root causes of obesity. Some experts suggest that genetics may play a role in someone’s propensity to become obese. In contrast, others claim that lifestyle choices are the primary factor. It is an important question to answer, as it could help us better understand how to address the obesity epidemic.
Childhood Obesity Is on the Rise

Much like adult obesity, childhood obesity is also on the rise worldwide. In the U.S., childhood obesity is a significant health concern. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 14.7 million U.S. youths aged 2–19 years have obesity.
The National Institutes of Health reports that approximately one-third of American children are overweight or obese. And what may be more concerning is that childhood obesity often leads to lifelong health problems. These include diabetes, breathing problems, high blood pressure, liver disease, skeletal problems, cholesterol, and heart disease.
Many factors contribute to childhood obesity, including genetics, unhealthy food environments, and lack of physical activity. The good news is that you can prevent, treat, and manage childhood obesity.
With the help of a healthcare professional, you can focus on maintaining a healthy weight, creating healthy eating habits, getting regular checkups, and providing more opportunities for physical activity.
Obesity and Blood Glucose Levels
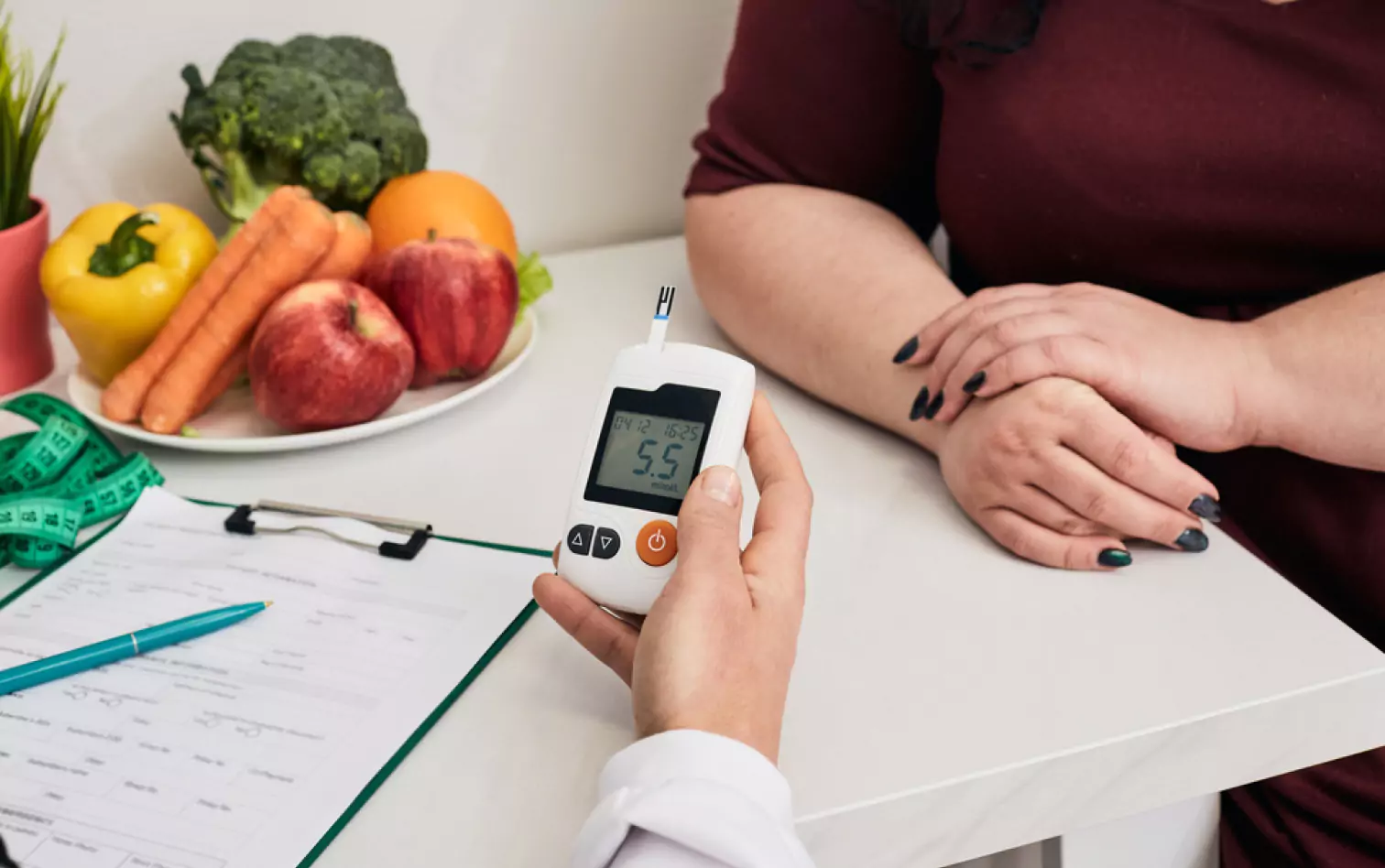

Glucose is a type of sugar that is the primary energy source for the body. The bloodstream carries glucose from the digestive system to cells throughout the body. Glucose levels are tightly regulated by the hormone insulin, which is secreted by beta cells in the pancreas.
Diabetes occurs when blood glucose levels become too high, as the body cannot produce enough insulin or does not use it properly. Obesity is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, and obese people often have higher blood glucose levels than those who are not obese. So, weight loss or maintaining a healthy weight may help control blood glucose levels in people who are obese and have diabetes. Of course, it’s best to check with a healthcare professional before making any drastic dietary or lifestyle changes, especially if you suffer from health problems.
Tips to Prevent Obesity
So, we know that obesity is a public health crisis and can be the leading cause of a range of health problems. But, there’s no need to panic. There are things you can do to prevent and reverse and manage obesity. If you’re concerned about your weight, or if you want to help a loved one manage or prevent obesity, here are some helpful tips:
Get Enough Physical Activity
The CDC recommends that adults get at least 150 minutes of physical activity a week. That breaks down to only 30 minutes a day, five days a week. The key to physical activity is starting slow and finding an activity that you think is fun. Physical activity is also key to preventing and managing childhood obesity.
Focus on Dietary Balance

Ditching fast food may be one way to eat healthily, but healthy eating is about so much more than that. Understanding what your body needs to fuel itself is important.
Finding a properly balanced diet for your caloric and nutrient needs can change your overall health and is especially valuable for obese people. It can be helpful to work with a registered dietitian to make a sustainable and nonrestrictive plan. Eating healthy doesn’t have to be hard.
Use Mobile Health Apps
An easy way to increase overall wellness and maintain a healthy weight is to use mobile health apps. Mobile health apps can help you track your diet and physical activity and provide support, encouragement, and accountability. They can also help doctors monitor progress among obese people and intervene if necessary.
Make the Most of CGM Technology

Monitoring your blood glucose levels using continuous glucose monitoring can help you understand how your body responds to your dietary and lifestyle choices. By understanding that data, you can make lifestyle changes like increasing physical activity, finding dietary balance, and creating healthier habits to maintain a healthy weight. It can also help you recognize your risk factors for and manage conditions like obesity.
Turn to Social Media
Another approach is using social media to promote healthy habits. Social media can be a powerful tool for information (don’t trust it all without consulting a healthcare professional) about everything from healthy dietary choices to physical activity. It can also help create communities of support for people trying to lose weight or get healthier.
Spreading awareness about the health risks associated with obesity can be an excellent first step to turning the tide on the obesity epidemic!
Find the right Nutrisense programto turn insight into progress.
Go Beyond Glucose Data with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall wellbeing. But viewing glucose isn't enough. Nutrisense, you’ll be able to learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
One-to-one coaching
Sign up to access insurance-covered video calls to work with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
Monitor and measure what matters
With the Nutrisense CGM Program, you can monitor your glucose with health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitor (CGM)s, and analyze the trends over time with the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.
Find your best fit
Ready to take the first step? Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.

Heather is a Registered and Licensed Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN, LDN), subject matter expert, and technical writer, with a master's degree in nutrition science from Bastyr University. She has a specialty in neuroendocrinology and has been working in the field of nutrition—including nutrition research, education, medical writing, and clinical integrative and functional nutrition—for over 15 years.


.webp)

