Can Good Oral Health Prevent or Lower Your Risk of Diabetes?

Key Takeaways
Diabetes is a health condition that can affect many different parts of your body, including your mouth. In fact, poor oral health is a common complication associated with diabetes. It can lead to a higher risk of gum disease, cavities, and even tooth loss. That's why it's crucial for people with diabetes to practice good oral hygiene and see a dentist regularly.
Diabetes often leads to high blood sugar, the leading cause of oral complications concerning the disease. By keeping your teeth and gums healthy, you can lower your risk for various oral health problems and may even be able to reduce your risk of developing health conditions like type 2 diabetes.
Luckily, there are some things you can do to improve your oral health and prevent further complications that arise from poor oral hygiene. Read on to find out more.
What is Diabetes, and How is it Connected to Dental Health?
Diabetes is a disease that affects how the body uses sugar. Your body breaks down the sugar in your food and drinks, or "carbohydrates," into glucose—the primary energy source for your body's cells.
The glucose your body produces then enters the bloodstream and travels to different parts of your body. You can experience health issues when your blood glucose levels are too high or too low. People with diabetes have to manage their blood sugar levels by monitoring and tracking them regularly. They also typically follow a diabetes management plan that includes medication, healthy foods, and physical activity.
High blood glucose levels can affect your white blood cell count, preventing your body from healing as quickly as it can when you have normal blood glucose levels. It's often the cause of the dental complications that are brought about by diabetes.
You may already know the difference between type 1, type 2, and prediabetes, but just in case, here’s a little refresher:
Type 1 Diabetes
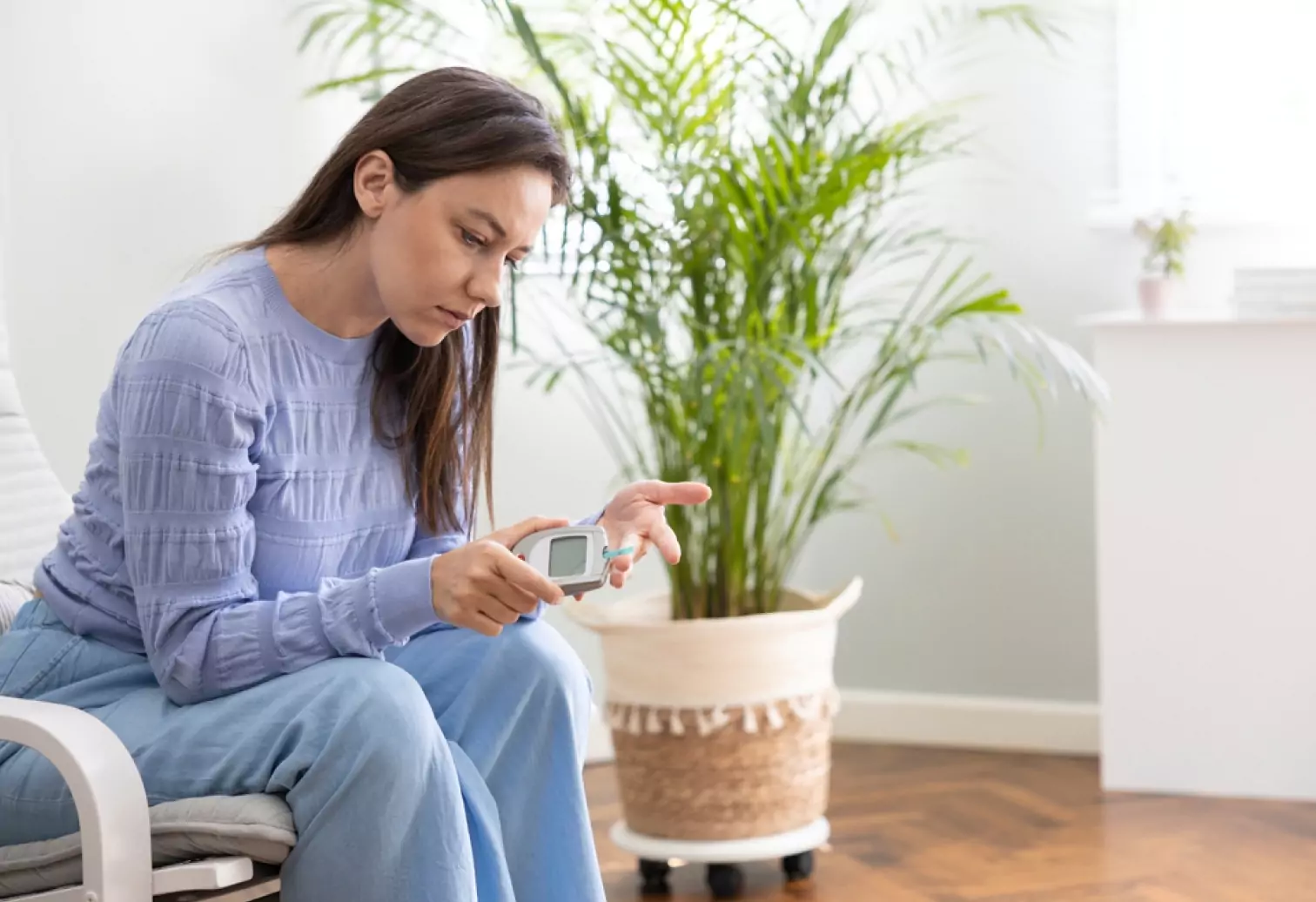

Type 1 diabetes is a condition that occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body use glucose for energy. Without insulin, the body cannot use glucose for energy, and blood sugar levels will become too high.
The symptoms of type 1 diabetes: Frequent urination, excessive thirst, extreme hunger, feeling tired all the time, nausea and vomiting, blurred vision, and weight loss. Taking insulin injections or using an insulin pump, eating a healthy diet, and regular exercise are some treatments for type 1 diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes
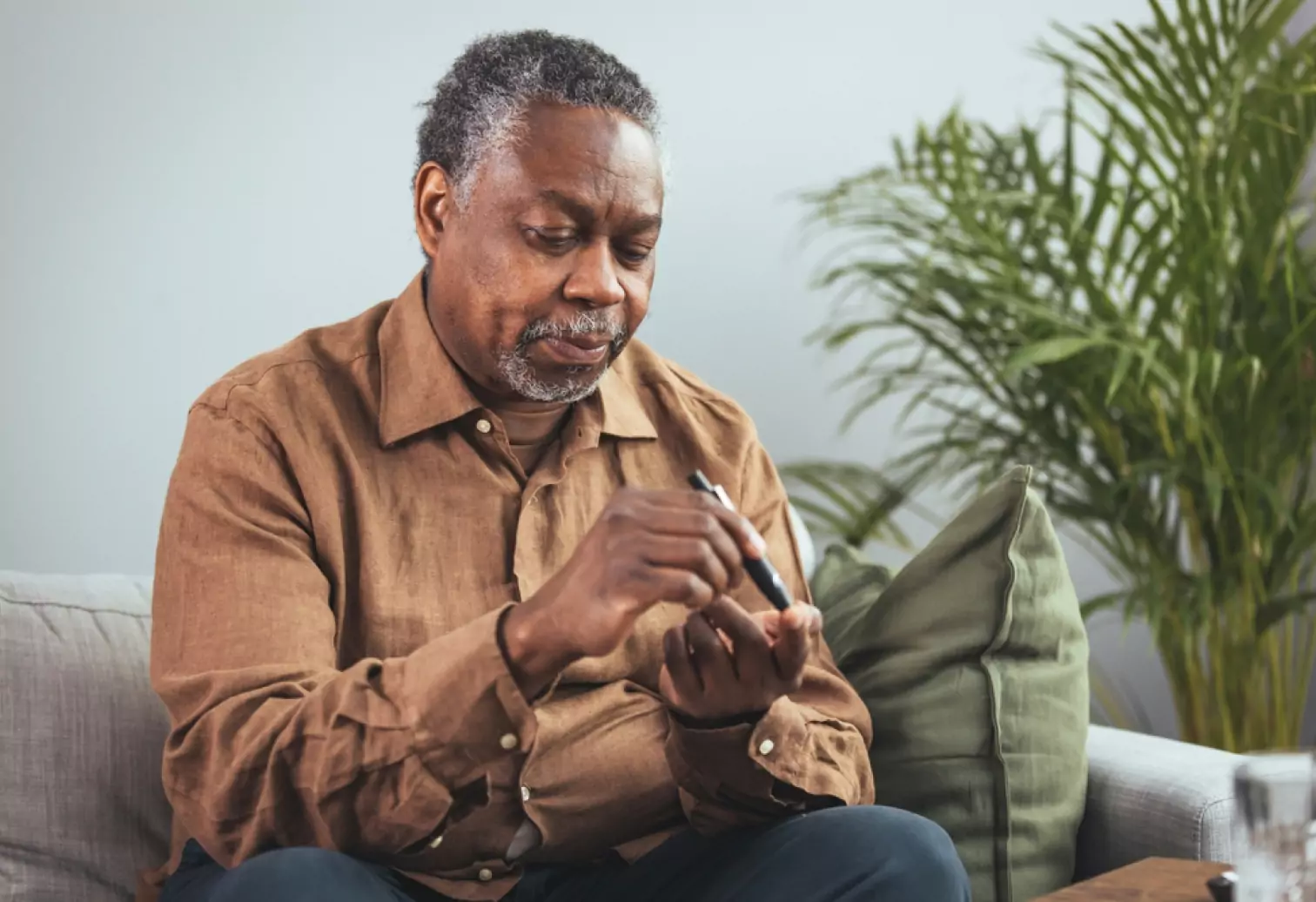

Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes sugar. Sugar, or glucose, is the primary source of energy for your body's cells and is necessary for them to function correctly.
This health condition develops when your body can't use insulin properly or make enough insulin to control blood sugar levels. Over time, high blood sugar levels can damage your heart, kidneys, nerves, and eyes. There is no cure for type 2 diabetes, but you can manage it with lifestyle changes and medication.
Prediabetes
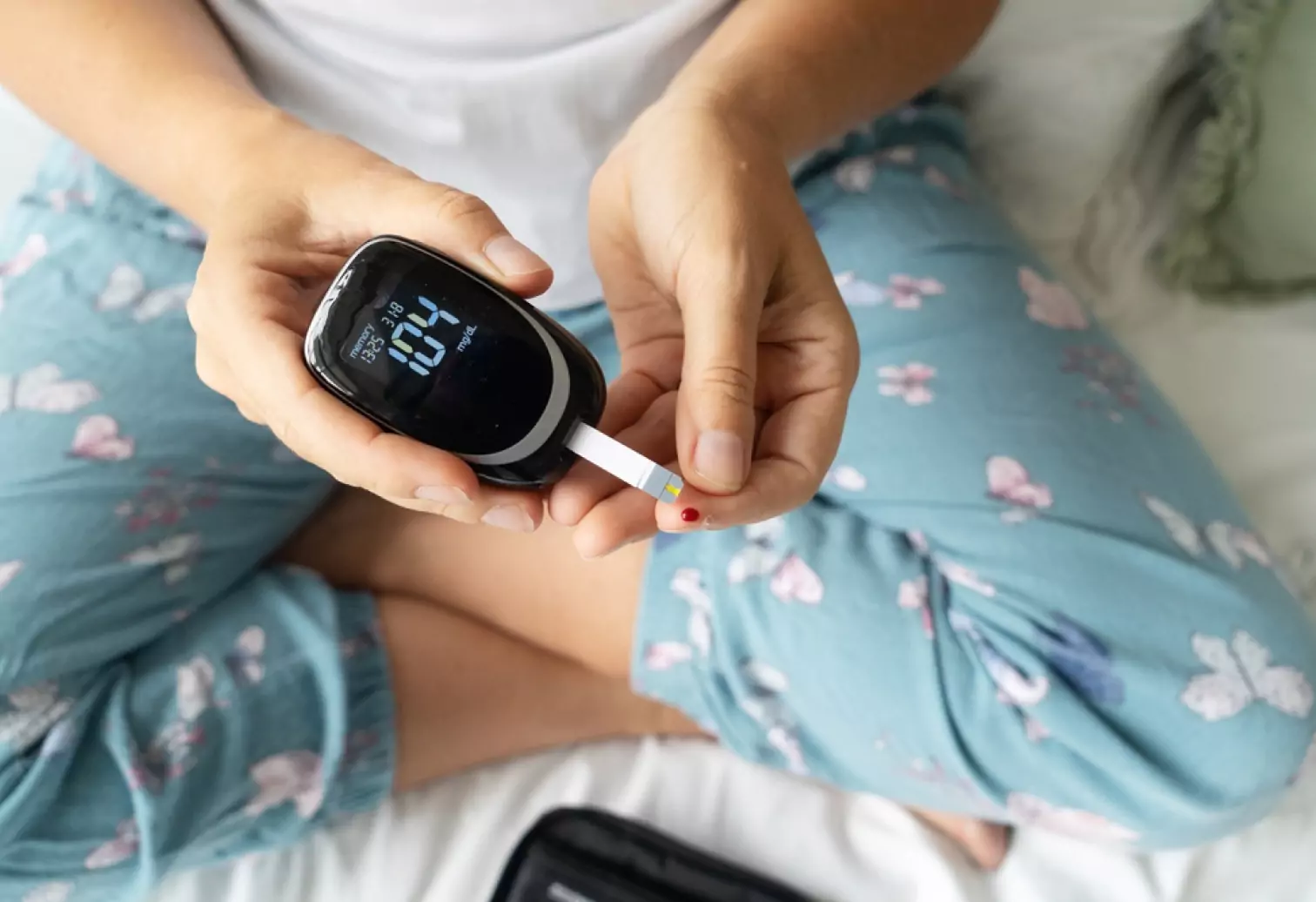
Prediabetes is when your blood sugar levels are higher than average but not yet high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. Having prediabetes puts you at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes and other health conditions like heart disease and stroke.
While it may seem milder than a diabetes diagnosis, prediabetes can still lead to some severe health issues if left untreated. The good news is that prediabetes is reversible, and making minor changes to your lifestyle can help reduce your risk of developing diabetes.
How Diabetes Can Affect Your Teeth and Gums
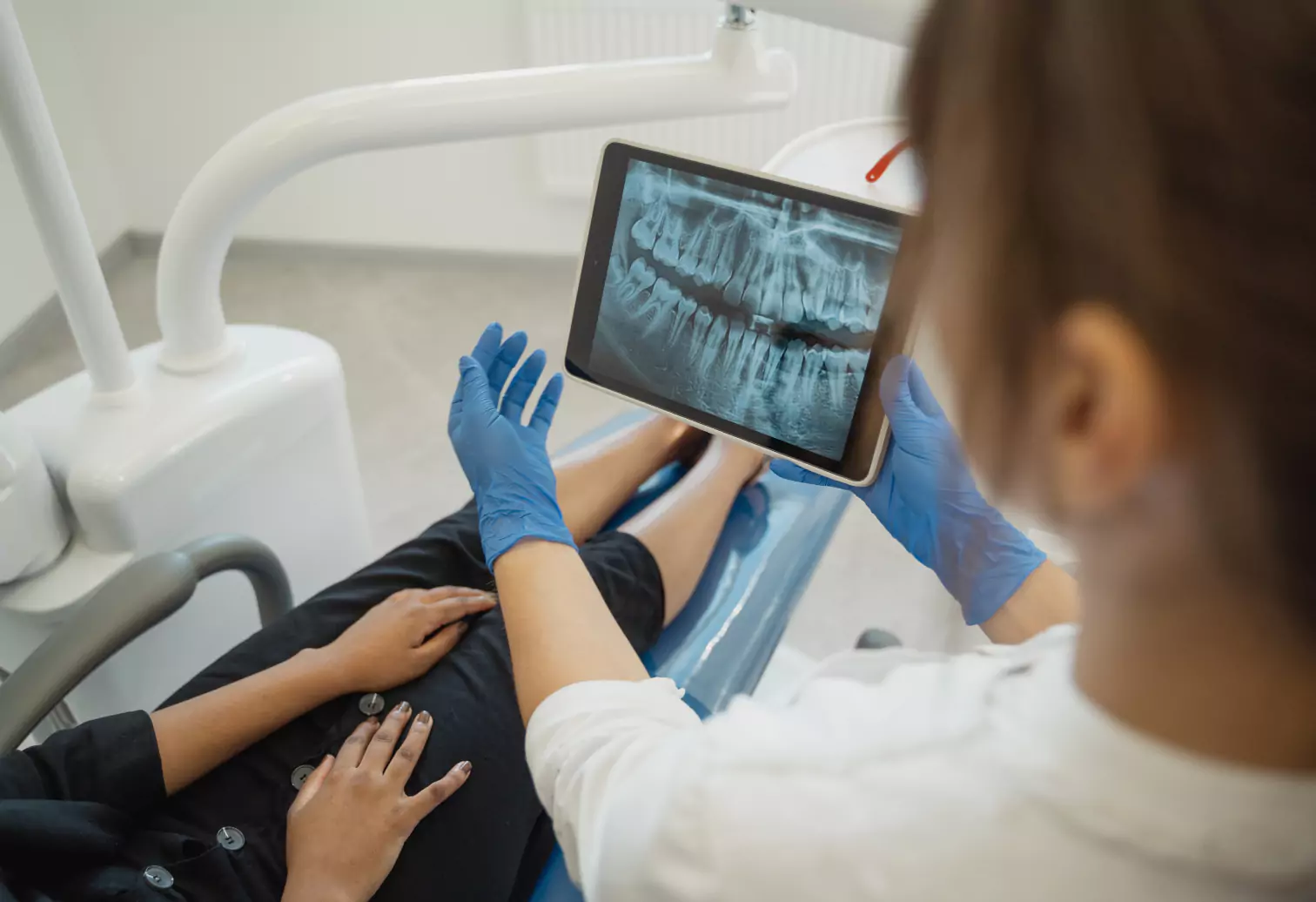
If you have diabetes, it's essential to be vigilant about your oral health. Diabetes can cause serious teeth and gum problems, so it's vital to protect them. But don't worry, with proper care and awareness, you can keep your smile healthy and beautiful!
Here are some of the most common ways that diabetes might affect your teeth and gums:
- Gum disease is more common in people with diabetes. Gum disease occurs when bacteria accumulate on the teeth and gums, causing inflammation and bleeding. Make sure to brush and floss regularly to prevent gum disease from developing.
- Diabetes increases the risk of tooth decay. The high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes create an environment that allows bacteria to thrive, leading to tooth decay.
- High blood sugar levels can cause plaque to build up on your teeth, leading to tooth decay. Remember: diabetes can change saliva and increase the amount of glucose in saliva, leading to plaque build-up on the teeth. Be sure to brush and floss after every meal and snack.
Diabetes and Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a common form of gum disease that can cause tooth decay, bad breath, and inflammation in the gums. Gingivitis is caused by bacteria that attach to the teeth and gums, and it can eventually lead to tooth loss.
If left untreated, it can lead to more serious forms of gum disease, like Periodontitis. Thankfully, Gingivitis is highly treatable with regular dental checkups and good oral hygiene.
If you’re worried about having Gingivitis, talk to your dentist. Early detection and treatment is the best way to prevent further damage.
Other Common Oral Health Complications for People with Diabetes

People with diabetes are at an increased risk of developing many oral health complications. Some of these complications can be relatively minor, while others can be more serious.
To keep your teeth and gums healthy, it’s best to be aware of the oral health problems that are most common in people with diabetes.
These are other common oral health complications found in people with diabetes:
Dry Mouth
Dry mouth, also known as xerostomia, is a condition that can occur when your saliva production decreases. While often temporary and not serious, dry mouth can be a bothersome symptom.
It can also lead to more severe problems, like difficulty speaking or eating, an increased risk for tooth decay, and trouble swallowing. Dry mouth is also common in people with diabetes. This can increase your risk for cavities and other dental problems.
Ensure that you stay hydrated if you have diabetes or are at risk of developing diabetes. When you have diabetes, your high blood sugar levels mean your body may produce less saliva. It can lead to dry mouth, which can cause discomfort and make it difficult to speak and swallow.
Thrush
Do you ever have a burning sensation in your chest or throat? Does it seem like the pain won't subside no matter what you eat, drink, or do? If so, you may be suffering from Thrush.
Thrush is an infection that affects many parts of the body, including the mouth, genitals, and skin, and will leave white patches where it manifests.
Though it's not a life-threatening condition, Thrush can be pretty uncomfortable. Diabetes can cause Thrush by weakening the immune system and making it more difficult for the body to fight off infection. If you have diabetes and develop Thrush, it's important to seek treatment.
Treatment typically involves antibiotics or anti-fungal medications. Taking steps to keep your blood sugar levels under control can also help prevent Thrush from developing in the first place.
Bleeding Gums
If you have diabetes, you may also be at risk of developing bleeding gums. This is because diabetes can cause damage to the blood vessels in your body, including those in your gums.
One of the complications of diabetes is poor blood circulation, which can make it harder for your gums to heal after an injury. When this happens, it's important to schedule a dental visit so that your doctor can determine the best course of treatment.
Good Oral Care Practices to Lower Your Risk of Developing Diabetes

When most people think of good dental care, they think of brushing and flossing their teeth. However, another vital part of oral hygiene is taking care of your gums. Did you know that the typical human mouth harbors around 500 to 700 bacterial species?
While some bacteria are beneficial, others can cause tooth decay, fungal infections, and other oral health problems. By following good oral hygiene practices, you can reduce the number of harmful bacteria in your mouth and keep your teeth and gums healthy.
Here are a few tips to help you get started!
- Make sure that you have a dentist-recommended toothbrush. This will help you maintain healthy teeth and control tartar and plaque build-up. Soft-bristled toothbrushes are often recommended for those who have diabetes.
- If you have dentures, it’s best to follow your health provider’s directions to clean and maintain them daily. A poor denture-care routine can lead to more bacteria in your mouth.
- Work with your doctor to ensure that you do everything you can to provide yourself with quality diabetes care.
- Schedule regular checkups with your doctor and your dentist to monitor how your diabetes might be affecting your dental health.
- Make sure to consult with your doctor about your diabetes and the effects it may be having on your dental health before scheduling treatment for periodontal disease. It will help your oral healthcare provider understand how to treat it.
- If you have or need braces, make sure that your dentist and orthodontist know about your diabetic condition. Cuts or damage caused by these devices may take longer to heal since people with diabetes can how a slower rate of wound healing.
- Remember that the rate at which your wound heals might take longer if you have diabetes. Make sure to follow your dentist’s post-treatment directions closely.
- The CDC recommends brushing your teeth with fluoride toothpaste twice a day.
Find the right Nutrisense programto turn insight into progress.
Go Beyond Glucose Data with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall wellbeing. But viewing glucose isn't enough. Nutrisense, you’ll be able to learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
One-to-one coaching
Sign up to access insurance-covered video calls to work with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
Monitor and measure what matters
With the Nutrisense CGM Program, you can monitor your glucose with health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitor (CGM)s, and analyze the trends over time with the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.
Find your best fit
Ready to take the first step? Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.

Katie is a dietitian at Nutrisense. With over 11 years of experience as a dietitian in many areas of nutrition, Katie has worked as a clinical dietitian within a hospital, as well as in the fields of diabetes, sports and performance nutrition, recovery from addiction, and general wellness. She’s also an athlete and has run 8 marathons, including the Boston Marathon.


.webp)

