Are Sardines Good for You?

Key Takeaways
Most oily fish may look unassuming but they typically have numerous health benefits. From mackerel and anchovies to pilchards, several of these fish are good sources of nutrients and minerals like vitamin B12, omega-3, magnesium, and more.
One of the most common of these types of fish is sardines—a small, oily fish eaten whole. You'll find them in the Mediterranean, Atlantic, and Pacific Oceans, and in abundance between peak sardine season in May and October. Despite their small size, the steel-blue fish have a nutritional profile that offers numerous health benefits. Anglers sometimes use sardines as bait for larger fish, but they're a popular food item in their own right.
Why Nutrisense Dietitians Love Sardines
Sold fresh, smoked, dried, and tinned—sardines are all excellent sources of healthy omega-3 fatty acids. They also contain magnesium, protein, potassium, selenium, and vitamins like vitamin B12; it's safe to say these little fish pack a big nutritional punch.
If you didn't grow up in a household that regularly ate sardines, they might be intimidating, thanks to their appearance and intense flavor. But we love them! We'd go so far as to say they'd be a pretty good contender on a list of superfoods.
Not convinced? Read on to learn about the potential health benefits of sardines from our expert registered dietitians and nutritionists. But first, here are some fun facts about the delicious oily fish.
Fun Facts About Sardines
- Sardines aren't a distinct fish species and are often used interchangeably with the term pilchard.
- Sardines are mostly common herrings, also known as Clupea harengus. Sometimes, other smaller-sized herrings are classified as sardines as well.
- A school of sardines is called a "family."
- Morocco is the largest exporter of canned sardines in the world.
- Love Worcestershire sauce? Did you know the main ingredient is fermented sardines?
- The term sardine is said to come from the Mediterranean island of Sardinia, once teeming with this type of fish.
- You likely know the term 'packed like sardines' comes from how the small fish are packed into tins. But did you know it's also the name of a children's game?
- Not all types of this small fish are endangered, but according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature, the Madeiran sardine is a vulnerable species.
- Cornish sardines have a Protected Geographical Indication status.
Fresh vs. Frozen vs. Canned Sardines—Does it Matter?

If you're looking for a healthy, affordable, and sustainable source of protein, sardines may be the perfect choice. However, with so many different types of sardines on the market, knowing which ones are the best option can be challenging.
Should you pick up a can of sardines? Should you forgo dried and tinned options for fresh sardines? And does any of this even matter? Take a look at what we found out.
Fresh Sardines
Fresh sardines aren't as commonly found as canned sardines, but they can be a good option if you find them. You can also prepare these little fish smoked, fried, baked, or grilled. If you're into Japanese cuisine, they serve sardines raw as sashimi, another way to enjoy this oily fish.
Frozen Sardines
Frozen sardines are the least common way to buy these fish in supermarkets. There isn't a big difference in buying them fresh or frozen as long as they were flash-frozen upon being caught, which helps with nutrient retention.
Canned Sardines
Canned sardines are the most popular bought and stocked types of Pacific sardines. The fish are washed and steam-cooked, dried, or fried before being tinned. Most have their gills and heads removed and are de-scaled. Some canned sardines have tomato, soy, and mustard sauce, but they're most commonly packed in olive oil or water.
What to Pick
We’re big fans of fresh fish, but fresh sardines are difficult to get your hands on. And while they're worth it if you do find them, don't miss out on this oily fish if you can't.
According to the Food and Drug Administration, sardines contain less mercury than most other fish. Even canned, they contain enough healthy fats to have several health benefits, including helping with heart disease and decreasing triglycerides.
So they're likely not terrible for you, even in their canned form. Of course, before changing your diet, determine what your body responds well to. It's best to consult a nutritionist or registered dietitian and use tools like continuous glucose monitors.
The Relationship Between Sardines and Blood Sugar Levels
Sardines have health benefits, are low in contaminants and toxins, and promote healthy bones and good heart health. But did you know they also impact your blood sugar levels? Can those with prediabetes and diabetes safely add sardines to their diets?
“Sardines are a healthy source of omega-3 fatty acids and protein. They can help regulate blood sugar levels and boost metabolic health. Remember, sardines are low in calories and rich in vitamins like vitamin B12 and minerals like zinc and magnesium. So, they make a healthy addition to any diet but may be particularly beneficial if you're trying to manage glucose or blood sugar,” says glucose-expert Amanda Donahue, MS, RD, CD.
Intermittent fasting has recently become a hot topic in the health world. It may hep control glucose levels, aid in weight loss, and positively affect your metabolism. If you've read up on or tried intermittent fasting, you know that one of the most important things to focus on is what you eat after your fast to break it.
Foods high in healthy fats (like omega-3 fatty acids) and protein are ideal for breaking your fast because they may not cause spikes in blood sugar levels for most people. They can also help satisfy hunger cravings and make you feel fuller for longer after you break your fast.
Feeling fuller for longer will prevent carbohydrate and sugar cravings and help boost your energy levels. Sardines, which are high in omega-3 fatty acids and contain protein, may be a great way to break your fast.
Are Sardines Good for Weight Loss
Are sardines fattening? Or, are sardines good for weight loss? If you’re wondering whether the fatty fish (or the fish oil) is a good addition to a weight management diet, here’s what you need to know: they may actually be helpful for your weight loss goals.
This tiny fish is low in calories and high in protein, making it an ideal choice for people trying to slim down. In addition, sardines are a good source of omega-3 fatty acids, which may help promote weight loss by reducing inflammation and preventing overeating. Some studies suggest that omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil may influence weight and fat metabolism, but their impact on weight loss appears modest and may vary among individuals.
It's important to note that incorporating fish oil into a well-rounded, healthy diet and physical exercise routine is more likely to contribute to overall well-being rather than serving as a standalone solution for weight loss.
Some Nutritional and Health Benefits of Sardines

Sardines are a rich source of essential nutrients like protein, omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, vitamin E, vitamin A, and vitamin D. The fatty fish is also low in mercury and other toxins, so it's no surprise they're considered a healthy option. Some research published by the National Institutes of Health also shows effects on cardiovascular health.
However, they also contain mercury (even though they have less mercury than other fish), so eat them in moderation.
Scientists have found that a diet heavy in fish consumption, like the Mediterranean and paleo diet, is ideal for most people's optimal health. But even with all the potential health benefits of sardines, it's best to find out if they suit your body.
If you can tolerate this type of fish, some reasons to include sardines in your diet are:
Calcium Content
If you're like most people, you probably think of milk and healthy bones when you think of calcium. However, a tin of sardines with the bones intact can also be a great source of calcium. The canning process softens the bones and makes them easy to chew along with the meat in canned fish.
Other cultures are known to create sardine stocks by cooking the bones in water or broth. Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the human body and is involved in many vital functions, including muscle contraction, blood clotting, and nerve transmission.
A Source of Minerals like Selenium and Magnesium
Minerals like potassium, phosphorus, zinc, iron, and magnesium play a role in many critical body functions. If you don't get enough of them, you could be at a higher risk for many health problems. Minerals are essential for many bodily processes, including maintaining fluid balance, transmitting nerve impulses, and building bones.
They also have anti-inflammatory properties and play a role in energy production. Fish contain iron and zinc, which are essential minerals for the human body.
Selenium is an essential mineral that your body needs for various functions. It may help protect against cancer, cardiovascular disease, and other health problems. In addition, selenium supports healthy thyroid function and helps keep the immune system strong. You can get selenium from foods like nuts, eggs, and fish or supplements if you're not getting enough through your diet.
Protein-Rich

In the fitness world, protein is king. And for a good reason: it's essential for repairing muscles and helping the body create new muscle tissue. Protein can also help you feel fuller longer, helping you maintain a healthy weight. It helps build and repair tissues, produces enzymes and hormones, and keeps your energy levels up. It also plays a significant role in regulating blood sugar.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Are you getting proper levels of omega-3 in your diet? You might not be if you're not eating fish or taking a supplement. These natural sources of nutrients are essential for your daily living for many reasons, including heart health, bone health, brain function, and inflammation reduction. Omega-3s also help your body lower triglyceride levels and may help prevent anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues.
Vitamins Like Vitamin D and Vitamin B12
Sardines are rich in many B vitamins, such as niacin and vitamins A, D, and B12. Vitamin B12 serves many functions. Not only is it needed for cardiovascular health, but it's vital for cognitive function, neuronal health, and DNA integrity. Vitamin D plays a role in countless functions, including regulating gene expression, bone mineralization, immune health, and so much more.
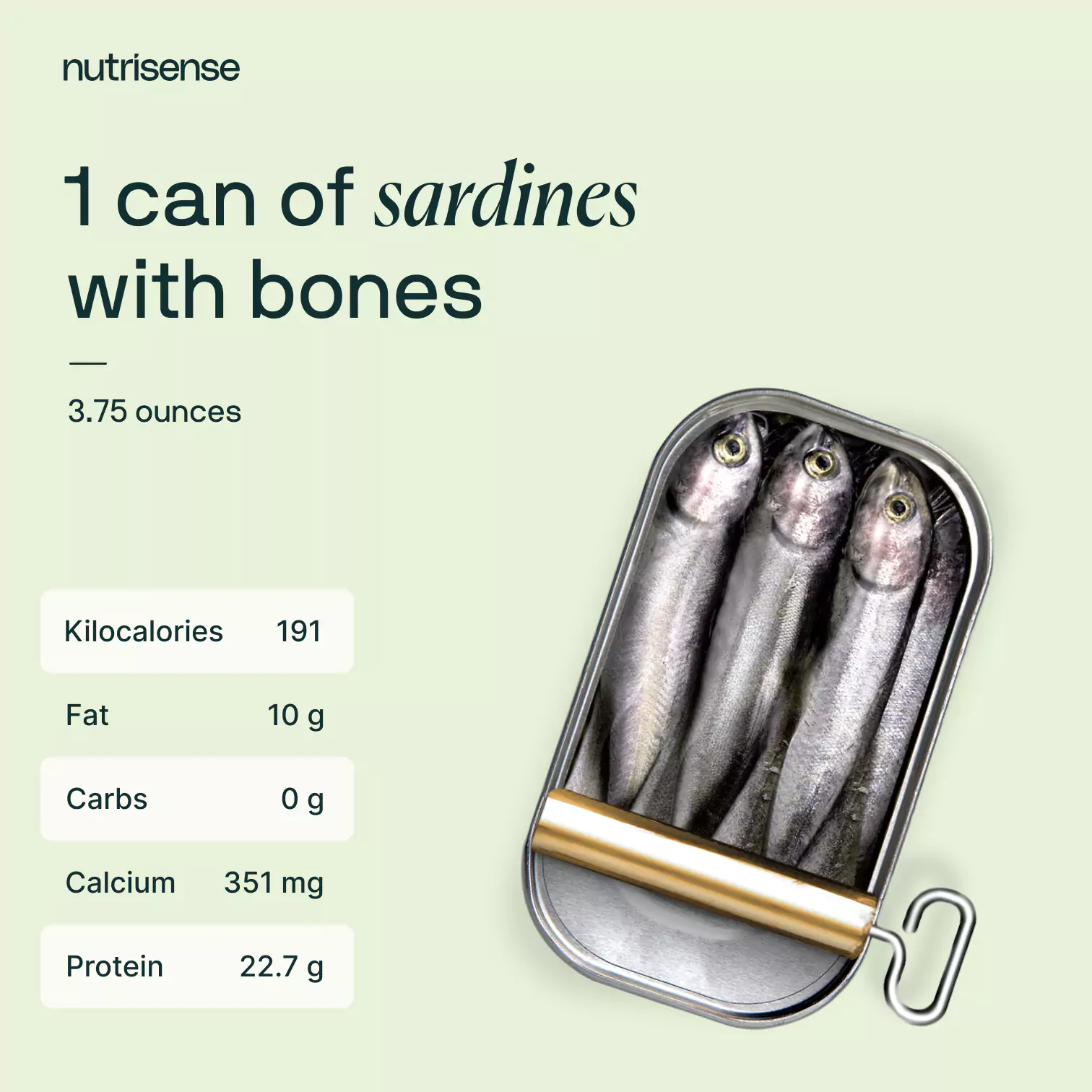
Different types of sardines have different nutritional content. But here's a good example of what you're getting in one can of sardines with bones.
How Often Can You Eat Sardines?

Can you eat sardines every day? Sardines are a great source of protein and omega-3 fatty acids, making them a healthy addition to your diet.
But how often should you eat them for the most benefits, and can you eat too many? Even though they have many health benefits, they contain some saturated fat (which may raise cholesterol levels for some). So, it's best to eat them in moderation—consider eating sardines two to three days a week, for example.
Sardines contain a small amount of mercury and other contaminants and toxins. But don’t worry! The FDA states that, as per the recommendations from Dietary Guidelines for Americans (which lists sardines in their "Best Choices" list of fish), sardines and sardine oil are safe to consume as part of a balanced diet. However, they do have uric acid, which can cause kidney problems in susceptible people or those with pre-existing conditions.
While they're typically safe for pregnant women to consume, everyone's body is different. So, it's best to talk to your doctor about whether this oily fish is for you.
What’s our takeaway from all of this? Overall, sardines can be a healthy addition to your diet. They're affordable and easy to find (well, canned sardines are, anyway!). And if you're looking for a healthy and delicious way to add more fish to your diet, they should be at the top of your list.
Find the right Nutrisense programto turn insight into progress.
Learn How Your Body Responds to Sardines with Nutrisense
If you want to know more about how your body reacts to fresh sardines, those marinated in olive oil, or canned sardines in tomato sauce, your best bet is to work 1:1 with an expert, like an on-demand or virtual dietitian. You'll get the best advice from a board-certified expert who knows how to work with your body's data, not just give you generic nutrition advice. Like Nutrisense's team of board-credentialed, glucose-certified dietitians and nutritionists, who work with you via insurance-covered video calls to figure out how foods like this fatty fish work for your body, based on your goals.
You can also get access to tools like glucose biosensors to keep track of your glucose levels. When paired with the Nutrisense app as part of the Nutrisense CGM program, you can see exactly how your body responds to various meals, including those with sardines. Working with a registered dietitian or nutritionist, you can make sense of this glucose data and get personalized recommendations to optimize your diet based on what works for you.
Start your journey to better health today by taking our quiz.
Go Beyond Glucose Data with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall wellbeing. But viewing glucose isn't enough. Nutrisense, you’ll be able to learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
One-to-one coaching
Sign up to access insurance-covered video calls to work with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
Monitor and measure what matters
With the Nutrisense CGM Program, you can monitor your glucose with health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitor (CGM)s, and analyze the trends over time with the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.
Find your best fit
Ready to take the first step? Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.

Amanda is a Nutrition Manager and Registered Dietitian, with a Masters in Dietetics from Stephen F. Austin State University. Originally from south GA, she got her undergrad degree from Texas Tech University. She worked at a hospital in Fort Worth, TX, for 4 years as a dietitian, counseling those living with HIV.




