Everything You Should Know About the Glucose Curve

Key Takeaways
Want to understand how your blood sugar levels (also known as blood glucose levels) respond to food, exercise, or stress? Your glucose curve—a visual pattern of your blood glucose levels throughout the day—holds the key. But what even is a glucose curve, and what do we mean when we say there's “no curve like yours?”
In this article, you’ll learn what a glucose curve is, what a healthy one looks like, how to interpret it, and how to flatten yours through food, exercise, and lifestyle changes. We’ll also walk through tips to monitor your glucose with health tech tools like CGMs (continuous glucose monitors) and glucose biosensors, and why you need a personal glucose-certified expert to help understand your personal trends.
What is the Glucose Curve?
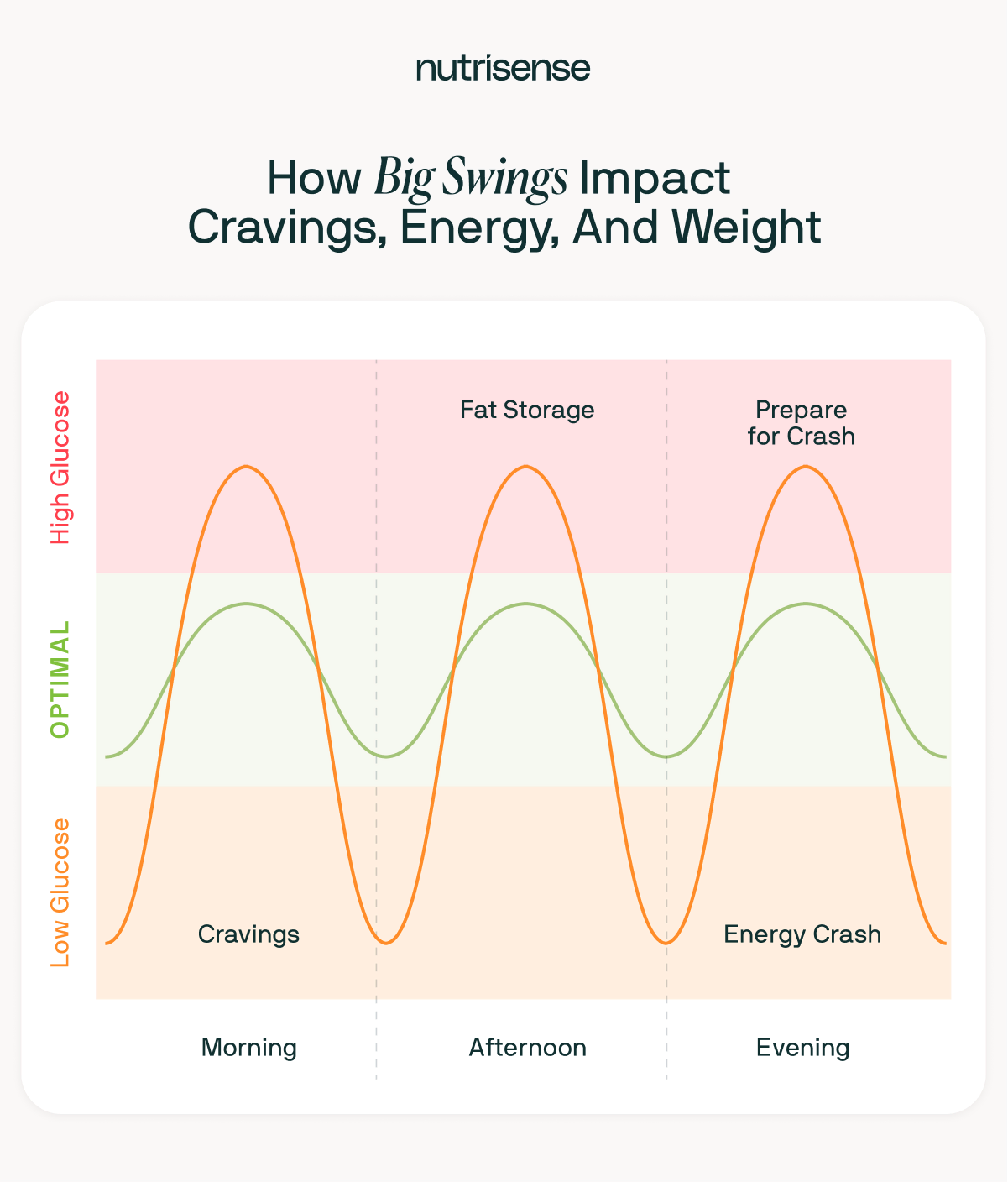
A glucose curve is a visual representation of how your blood glucose levels rise and fall over time, especially after meals, stress, or physical activity.
You’ll typically see a curve that rises after you eat and falls as insulin helps your body use or store glucose. The goal is a gentle rise and return to baseline—sharp spikes and crashes can signal metabolic dysfunction.
Glucose curves are a graphical representation or chart typically tracked in mg/dL (US) or mmol/L (internationally), and can be monitored with glucose monitoring devices, a glucometer, or lab tests. Understanding your blood glucose curve can help identify glucose spikes, dips, and signs of insulin resistance.
{{rich-text-newsletter="/style-guide"}}
What Does a Healthy Glucose Curve Look Like?
A healthy glucose curve:
- Rises gradually after eating (peaks around 30–60 minutes)
- Peaks below ~140 mg/dL
- Returns to pre-meal levels within two to three hours
- Has minimal post-meal crashes (dips below 70 mg/dL)
The smoother and more stable the curve, the better your body is at handling glucose. Repeated sharp spikes and dips may signal poor glucose tolerance, insulin resistance, or a diet high in ultra-processed carbs.
The Science Behind Glucose Curves
Glucose metabolism is how your body processes blood glucose—a type of sugar that serves as your cells' main energy source. After you eat, your digestive system breaks food down into simpler sugars like glucose. That glucose then enters your bloodstream, causing your blood glucose levels to rise.
When blood glucose rises (elevated blood glucose levels lead to a state called hyperglycemia), your pancreas (which produces the hormone glucagon) releases insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps move glucose out of the blood and into your cells, where it can be used for energy or stored for later. This insulin effect is how your body brings glucose levels back down into a healthy range.
The glucose curve shows this process visually. After eating, your blood sugar typically rises, creating a curve that peaks and then falls. The speed and size of this curve depend on many factors, including:
- .What you ate
- How much insulin your body produces
- How sensitive your cells are to insulin
- Your individual metabolic rate
Once insulin kicks in, your glucose levels decline. A healthy curve reflects a smooth rise and gradual return to baseline, while a sharp spike or slow recovery may suggest metabolic inefficiencies like insulin resistance.
Factors Affecting Glucose Curves

Everyone’s glucose response is different. While there are general patterns in how the body handles glucose, your curve is shaped by unique factors like your bodyweight, diet, exercise habits, stress levels, sleep quality, medications, and genetics.
That means someone else’s “normal” may not reflect how your body processes glucose. Here’s a breakdown of key factors that influence your glucose curve:
What You Eat and When You Eat
What and when you eat can significantly impact your glucose curve by affecting how much and how quickly your blood glucose levels rise and fall. For example:
- Meals that are high in carbohydrates, especially those with simple sugars and refined grains, tend to cause a rapid and sharp increase in blood glucose levels.
- Meals with a lower carbohydrate content or those that contain complex carbohydrates, fiber, and healthy fats tend to result in a slower and more gradual rise in blood glucose.
- Including protein in your meals can help slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, leading to a more gradual and sustained release of glucose into the bloodstream.
- The timing of your meals can also influence the glucose curve. Eating regular, balanced meals throughout the day helps maintain more stable blood glucose levels compared to irregular or skipped meals.
How You’re Exercising and How Often You’re Exercising
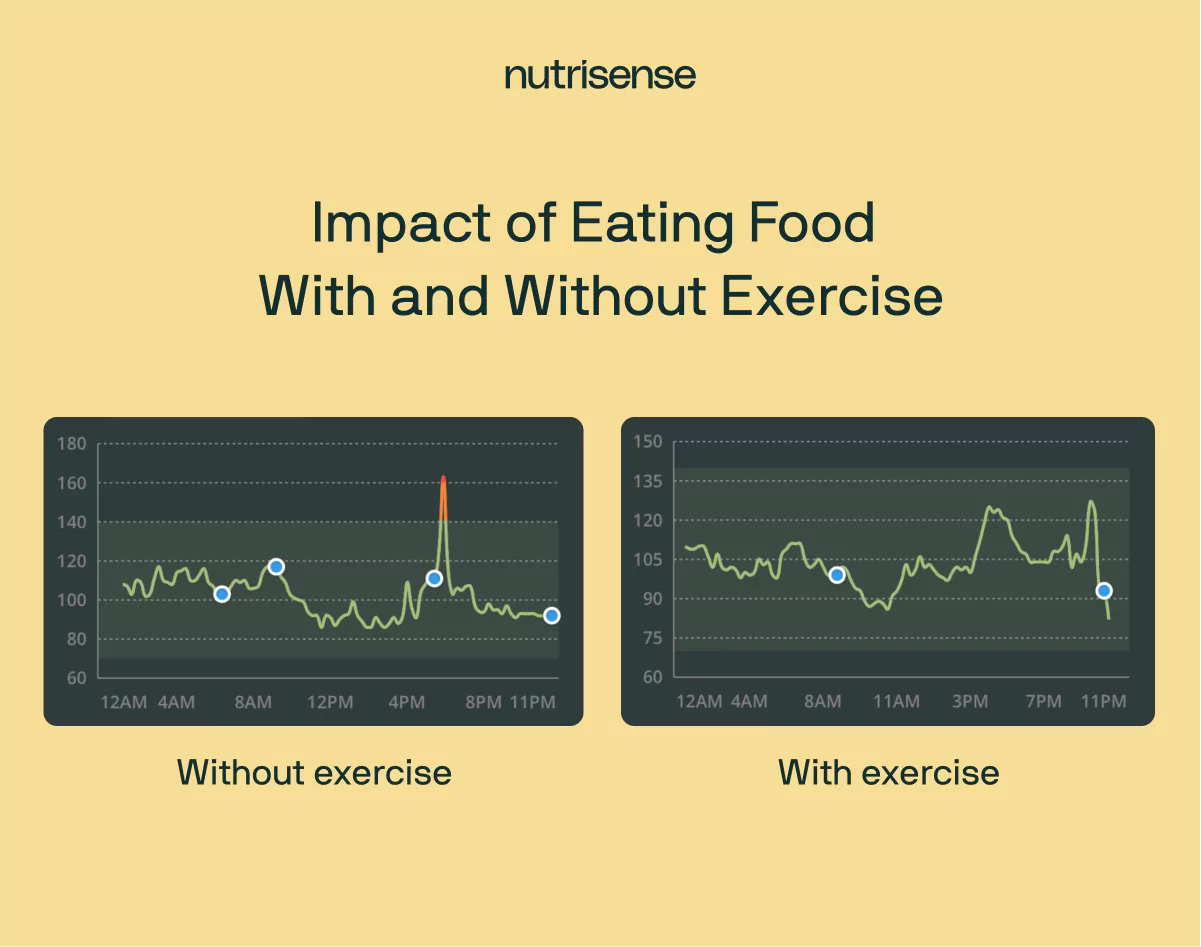
Exercise influences glucose levels by increasing glucose uptake and improving insulin sensitivity. When you’re active, your muscles contract and demand more energy. To meet this demand, your body pulls glucose from the bloodstream—lowering blood glucose concentrations in the process.
This increased muscle glucose uptake helps reduce and stabilize blood sugar levels, leading to a flatter, more controlled glucose curve.
Beyond the immediate effect, regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, meaning your cells respond more efficiently to insulin. As a result, your body can clear glucose from the blood more effectively—even hours after exercise ends.
Together, these effects contribute to improved glucose metabolism and smoother curves throughout the day.
Medications You’re Taking
Certain medications influence glucose regulation and your glucose curve by altering insulin function, glucose production, or cellular uptake.
- Antidiabetic medications like insulin, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and oral hypoglycemic agents help lower blood glucose levels by enhancing insulin action or reducing glucose production. For those taking insulin, the timing and dosage of insulin—also known as your insulin dose—directly impacts how your glucose curve rises and falls after meals.
- Glucocorticoids (e.g., prednisone, cortisone) increase blood glucose levels by stimulating hepatic glucose production, inhibiting glucose uptake in cells, and impairing insulin signaling.
- Other drugs, including beta-blockers and some antidepressants, may indirectly affect glucose levels by disrupting hormones that regulate glucose balance.
If you're tracking your glucose curve, it's important to consider how any medications you're taking may be influencing your results.
Stress and Sleep

Stress and sleep impact glucose metabolism through hormonal regulation.
When you experience stress, your body releases cortisol and other stress hormones. Cortisol triggers gluconeogenesis (glucose production in the liver) and reduces cellular glucose uptake, leading to elevated blood glucose—even without eating.
Chronic stress can lead to sustained high cortisol levels, which impairs insulin sensitivity and contributes to more frequent or prolonged glucose spikes, contributing to higher blood glucose levels over time. It can also lead to insulin resistance.
Sleep deprivation has similar effects. Poor sleep disrupts the balance of hormones like leptin and ghrelin, increasing hunger and cravings for high-carb foods. It also lowers insulin sensitivity, making it harder for your body to regulate glucose efficiently.
Together, stress and inadequate sleep can result in higher, more erratic glucose curves.
Genetics
Your genetic makeup plays a foundational role in how your body processes glucose.
- Some people inherit variations in genes that influence insulin production, affecting insulin secretion, insulin receptor function, or the activity of glucose transporters like GLUT4.
- These genetic differences can alter how quickly or effectively glucose is moved from the bloodstream into cells, shaping both the peak and recovery phases of your glucose curve.
While you can’t change your genes, knowing your individual tendencies—like a predisposition toward insulin resistance—can help guide more personalized strategies for glucose management.
The Importance of Monitoring Your Glucose Curves
In the United States, recent studies suggest that only 12 percent of Americans are considered to be metabolically healthy. Tracking and monitoring your glucose curves can help you better understand your overall metabolic health and implement healthy lifestyle changes.
Your glucose levels provide valuable insights into how your body responds to various foods, activities, and lifestyle choices that make up your daily routine. By tracking your glucose levels over time, you can identify patterns, trends, and potential triggers that may affect your blood glucose control.
Keeping your glucose levels within a range of 70 to 140 mg/dL through the majority of the day may reduce the risk of developing conditions such as prediabetes or type 2 diabetes.
This information empowers you to make informed decisions about your diet, exercise routine, stress management, and other lifestyle factors that directly impact your glucose metabolism, allowing you to make proactive choices to support your overall well-being.
5 Tips for Interpreting Glucose Curves
There are a few different ways to go about blood glucose measurement. Whether you use a glucometer, a continuous glucose monitor, or a blood sample, interpreting your glucose values allows you to gain insights into your body's response to various lifestyle factors and make informed health decisions.
Here are some useful tips for interpreting your glucose curves:
1) Track and Monitor Glucose With a CGM
Using a tool like a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) or glucose biosensor can be a game-changer in glucose monitoring and management. While these glucose monitoring sensors don’t measure blood glucose levels directly, they provide 24/7, continuous data on your interstitial glucose, which offers a comprehensive picture of how your body responds to different foods, activities, and lifestyle choices.
These glucose sensors can capture fluctuations and trends in glucose levels throughout the day, revealing valuable insights that can help you make changes that support a healthy lifestyle.
If you're looking to start your journey with a CGM and explore the benefits of continuous glucose monitoring, consider trying Nutrisense’s CGM program. Nutrisense offers user-friendly CGM solutions, expert guidance from credentialed glucose experts, and personalized insights to help you make informed choices about your health and work toward your metabolic goals.
Take control of your glucose levels with Nutrisense and embark on a transformative path to better health. Take our quiz to learn more and start your CGM experience today.
2) Identify Postprandial Spikes and Their Implications
Postprandial glucose refers to the concentration of blood glucose levels in the blood after consuming a meal or food. Postprandial glucose levels are influenced by several factors, including the composition of the meal (carbohydrate, protein, and fat content), portion size, rate of digestion and absorption, individual metabolism, and the body's ability to produce and utilize insulin.
After-meal glucose spikes can indicate poor glucose control and may increase the risk of long-term complications associated with diabetes.
3) Analyze Glycemic Variability and its Impact on Overall Glucose Control
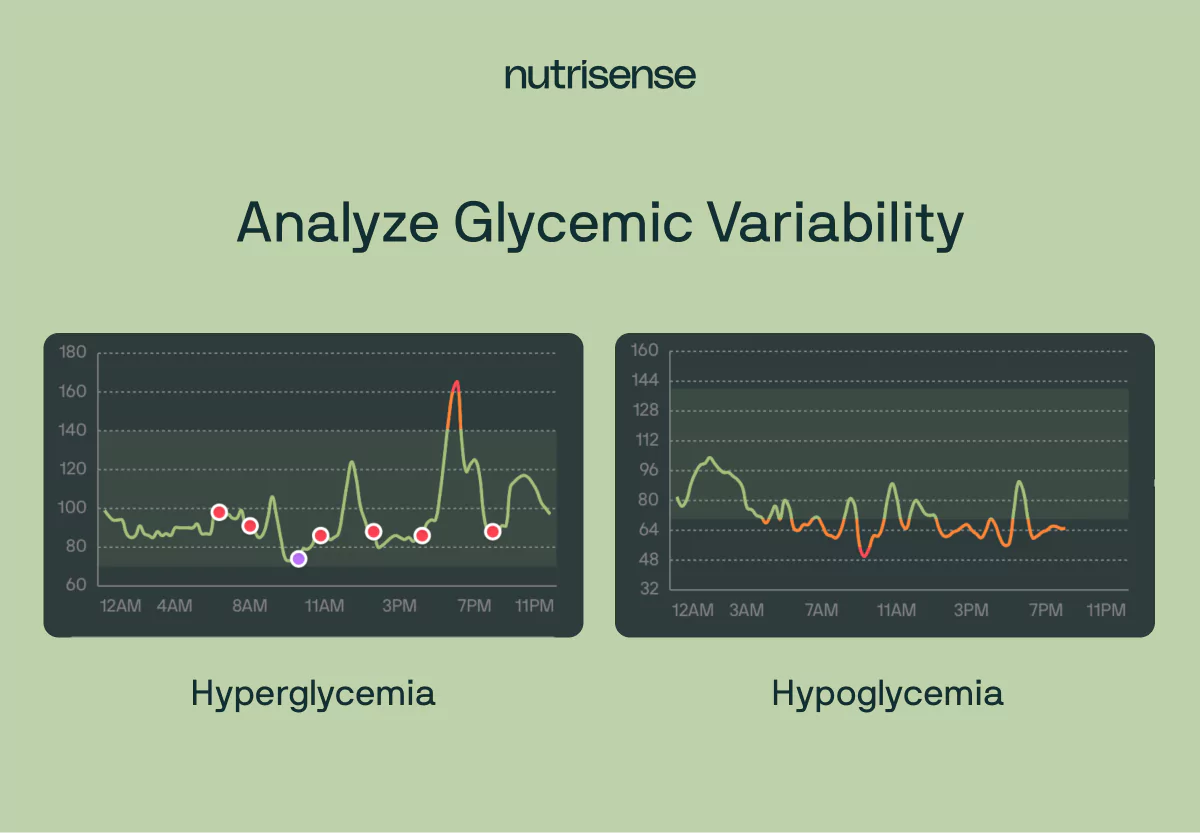
Glycemic variability refers to the swings and fluctuations of blood glucose levels over a given period of time. Glycemic variability is measured by analyzing the range, amplitude, frequency, and duration of blood glucose fluctuations.
High glycemic variability is characterized by significant swings in blood glucose levels, with frequent spikes and drops. Low glycemic variability suggests more stable blood glucose control with minimal fluctuations.
Interpreting glycemic variability helps you gain a better understanding of how various factors, including meals, exercise, stress, and medication, influence your glucose control and helps you to make needed changes to your lifestyle.
4) Consider Fasting and Basal Glucose Levels For a Comprehensive Understanding
Every individual has unique fasting and basal glucose levels that may vary depending on factors such as age, health conditions, and medication use. Considering these will help adjust to what’s right for you.
- Fasting glucose levels, measured in the morning before eating or drinking anything, provide a baseline reference point for glucose control. This is sometimes measured using an oral glucose tolerance test. They represent the body's glucose levels after an extended period of not consuming food. Comparing postprandial glucose levels to the baseline helps identify the impact of meals on blood glucose response.
- Basal glucose levels refer to stable, overnight glucose levels. These levels reflect the body's ability to maintain glucose homeostasis when no external factors are significantly influencing blood glucose levels.
Understanding basal glucose control is important to help check your body's overall glucose regulation outside of meal and lifestyle-related effects.
5) Consult a Glucose-Certified Nutrition Professional
Having access to glucose insights is one thing, but understanding how to interpret them and integrate that information alongside your unique personal health and medical history is another. Working with a qualified nutritionist such as a registered dietitian or certified nutrition specialist can make it easier to understand what foods may be having a poor impact on your health.
With Nutrisense you get access to insurance-covered video calls with a certified specialist to help you set attainable health goals and create a plan for reaching them. Having a trustworthy and highly trained nutritionist to guide you can not only help hold you accountable, but they can also guide you in building sustainable habits for reaching your goals.
How to Flatten Your Glucose Curve
Want to reduce spikes and smooth out your glucose curve? There are many reasons to do this, including preventing or managing prediabetes or T2D (type 2 diabetes mellitus). Our experts suggest starting with these practical strategies:
Build balanced meals for yourself:
- Prioritize protein, healthy fats, and fiber
- Limit refined carbs and sugary drinks
Remember to move after your meals:
- A short walk after meals can significantly reduce postprandial glucose
Stress less and sleep more:
- Practice stress reduction (breathwork, therapy, mindfulness)
- Aim for seven to nine hours of sleep per night
Monitor and track your glucose curve and patterns:
- Glucose monitoring isn’t just for diabetic patients. Use a glucose monitor or glucose biosensor to identify personal triggers.
- Work with a glucose-certified expert to compare how different meals affect your glucose curve.
CGM vs Glucometer: Which Helps More?
For many reasons, using a continuous glucose monitor or glucose biosensor can be a better idea than a glucometer to help monitor and track your glucose curve. Here’s just one reason:
- With a glucometer, you get single readings at singular time points, which means limited context.
- With a CGM or glucose biosensor, you can get 24/7 feedback that shows the full glucose curve.
As you can see, continuous glucose monitoring is a better idea, since it’s ideal for understanding patterns, testing meal responses, and catching overnight or hidden spikes.
FAQs: Glucose Curve Basics
What is a normal glucose curve after eating?
A gradual rise peaking within one to two hours, followed by a steady return to baseline in two to three hours.
What causes blood sugar to spike?
There are many reasons, and since there's no one-size-fits-all, it's best to consult a professional to find out why yours is. Some reasons you can look into in the meantime include simple carbs, large portions, poor sleep, stress, or lack of activity.
How do I flatten my glucose curve?
Eat balanced meals, move after eating, reduce stress, and track patterns with a CGM.
What does it mean if I crash after meals?
You may be experiencing reactive hypoglycemia—often caused by large insulin responses to high-carb meals.
Every Glucose Curve is Unique
As you can see, there are a wide range of factors that can influence your glucose curve throughout the day and impact your glucose trends over time. That’s why it can be so beneficial to learn more about how your unique body responds to your diet and lifestyle habits, since what works for one person may not have the same effect on you.
To help inspire and motivate you on your journey, we often highlight the stories of our members and partners conducting glucose experiments to see how different types of food and lifestyle activities impact their glucose levels. Follow us on Instagram too, to check more of them out!
The Nutrisense program is designed to help support you on your wellness journey through 24/7 insights and expert guidance. If you’re ready to conduct your own glucose experiments and take control of your health, start today by taking our quiz.
Find the right Nutrisense programto turn insight into progress.
Go Beyond Glucose Data with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall wellbeing. But viewing glucose isn't enough. Nutrisense, you’ll be able to learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
One-to-one coaching
Sign up to access insurance-covered video calls to work with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
Monitor and measure what matters
With the Nutrisense CGM Program, you can monitor your glucose with health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitor (CGM)s, and analyze the trends over time with the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.
Find your best fit
Ready to take the first step? Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.

Liz has a Master of Science degree in Clinical Nutrition and Integrative Health and is a board-certified nutrition specialist (CNS) and a licensed dietitian nutritionist (LDN). As a nutritionist, Liz has educated and counseled 100s of clients in areas such as weight loss, hormonal imbalances, and gastrointestinal diseases.




