What Diet Is Best for Me? 8 Healthy Diets to Consider

Key Takeaways
At the beginning of a new year, many people enjoy making new year’s resolutions and setting goals to improve their health over the coming year. If this sounds like you, there’s also a good chance that you may be considering trying out a new diet to help you reach those goals.
Unfortunately, many diets are notorious for being hard to sustain over a long period of time. Plus, with all the false health claims out there, how can you know which diet plan will be effective for you and your wellness goals?
In this article, we’ll outline the effect that eight popular diets may have on the body, how they might benefit your health, and some of the reasons you might choose each one.
How to Choose the Right Diet for You
Everyone’s body is different–this concept is known as biological individuality. When choosing the best diet for you, you’ll want to keep in mind that something that was effective for someone else might not give you the same results.
There are many different factors that you’ll need to consider before choosing a diet. These include:
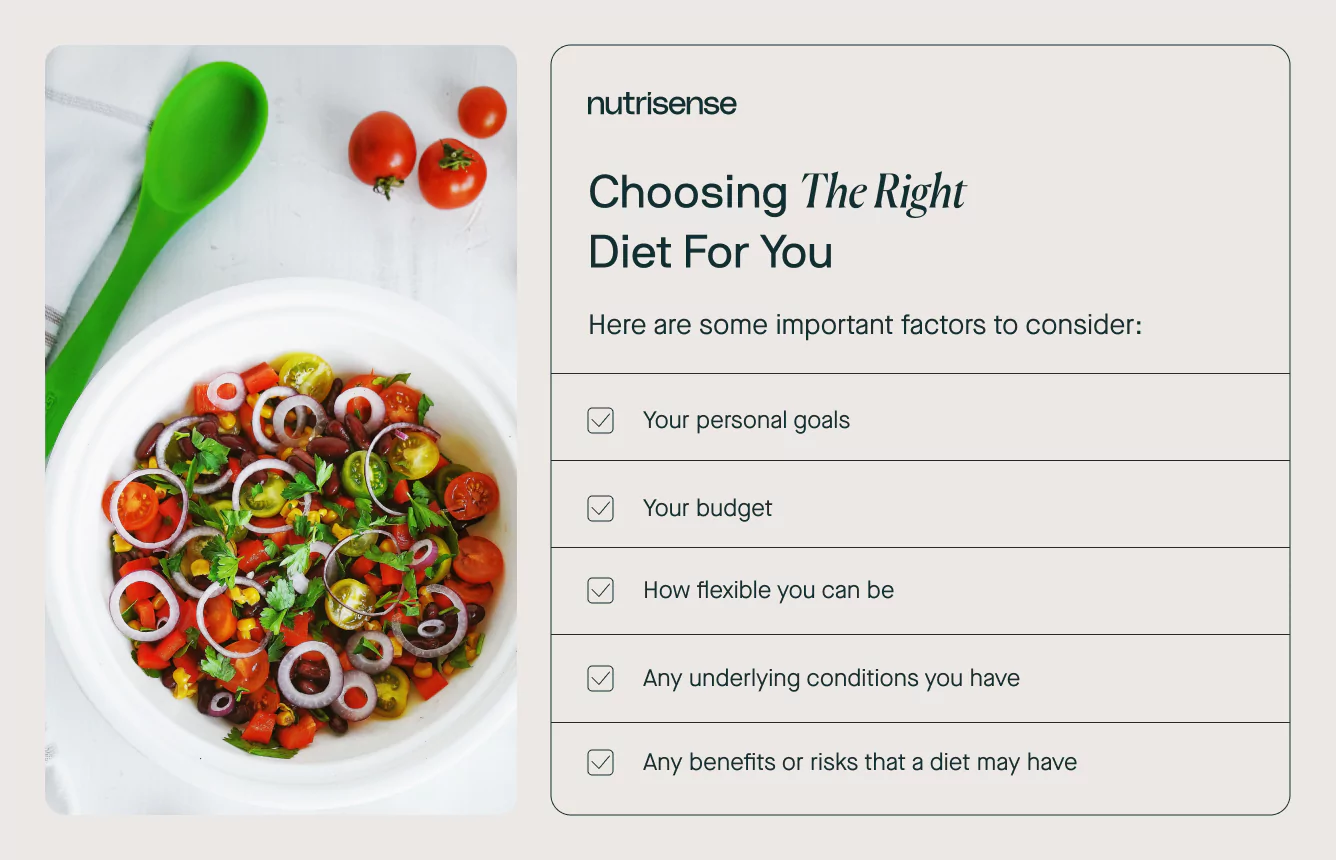
Here’s why each of these factors is important to take into account before starting out on a new diet.
Personal Goals
The first and most important step to deciding which diet to try is to ask yourself what your intention is. Is your goal…
- To lose weight?
- To simply learn about your body?
- Related to supporting a health condition such as hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)?
Different eating plans are designed to achieve different results. Knowing what your goals are empowers you to choose a diet that can help you to effectively achieve them.
Budget
Any dietary approach needs to fit within your budget to be sustainable. When starting a new way of eating, make sure you can avoid straying outside of what you can afford.
Flexibility
Adopting a new way of eating can be easier if you cook at home often and have more control over the ingredients you’re using. But what about dining out? Flexibility is an important part of creating sustainable diet and lifestyle changes.
With a little practice, however, you’ll become an expert at interpreting menus and knowing what aligns with your dietary goals when you’re out and about.
Underlying Conditions

Underlying conditions can also have an affect on factors such as weight gain, difficulty losing weight, or ability to exercise. Understanding how your body responds to different foods can help you to figure out what type of diet is most sustainable for your individual needs.
{{rich-text-cta-wl1="/style-guide"}}
Benefits and Risks
Before choosing a new diet, it’s important to have a good understanding of your personal health and any potential benefits or risks that changing your eating habits may have.This may be especially important if you have an underlying health condition.
Consult your doctor and registered dietitian for guidance before making any significant dietary changes.
Metabolic Diets
The goal of many diets advertised as being “metabolic diets” is typically to increase your basal metabolic rate (BMR). This is the baseline amount of calories your body needs to function while at rest and can impact factors such as weight loss.
Your metabolic rate depends on a number of factors, such as:
- Age
- Sex
- Amount of fat-free mass
- Physical activity levels
- Hormone levels
Let’s take a look at a few of the most common so-called metabolic diets and what health benefits they may have.
1) The Metabolic Typing Diet

The Metabolic Typing Diet was first introduced through a book called “The Metabolic Typing Diet” in 2001. It aims to define an ideal ratio of macronutrients for your body based on your genetics and body type.
According to the book, there are three metabolic types: ectomorph, mesomorph, and endomorph. These types help to determine what types of macronutrients to focus on in your diet based on your unique metabolism.
Once you identify your metabolic type, you’ll focus on either a high protein or high carb diet.
Benefits
There is some evidence that metabolic typing, also called metabotyping, may help to identify your level of risk for cardiometabolic diseases. Some researchers also believe it may be possible to improve different areas of your health through a more personalized diet.
Downsides
There isn’t much evidence supporting the effectiveness of this diet. There’s good evidence to show that some body types will have better health outcomes with the recommended macronutrient changes. More research is still needed to determine who can benefit from this type of diet.
Flexibility and Budget
This diet is relatively easy to be flexible with since it does not require you to restrict certain foods. Instead, based on your metabolic type, you’ll either focus on eating either fast or slow-digesting foods to reach your goals.
Because this diet is very easy to customize within your macronutrient targets, it’s not likely to break the bank.
2) The Zone Diet

You might recognize the name of this diet from products on the shelves at some grocery stores. The idea behind the Zone Diet is to reduce inflammation to support hormonal communication on a cellular level.
Similarly to the Metabolic Typing diet, the Zone Diet advises that you follow a specific macronutrient breakdown. On the Zone diet, you will consume 40 percent of calories from carbs, 30 percent from protein, and 30 percent from fat.
According to its creator Dr. Barry Sears, getting into “the Zone” will help regulate your hormone function.
Benefits
The Zone Diet claims to reduce inflammation, which can contribute to stubborn weight loss plateaus and may increase your risk of developing certain health conditions.
In addition to the macronutrient ratio proposed by this diet, you’ll be encouraged to eat lots of whole, unprocessed foods. There are no firm restrictions as to which kinds of foods you can consume, which can make it easier to follow this diet over a long period of time.
Downsides
This low-calorie diet restricts calories to 1,200 per day for women and 1,500 per day for men, which is extremely low for much of the general population. Because of this, you should work with a dietitian or healthcare professional to make sure you are meeting your caloric needs.
A common misconception is that expending more calories than you consume is the only way to lose weight. While the ratio of calories in to calories out matters, it’s not the whole story.
Undereating can cause slowed metabolism, and may even lead to immune and digestive problems, and hypoglycemia, among other health concerns.
Flexibility and Budget
As we mentioned earlier, this diet is a relatively flexible option as you have the freedom to select foods based on your preference as long as they fit within your macronutrient ratio. This means that you can easily craft this diet to fit inside your personal budget.
The Zone Diet is also accommodating for vegetarians and those who are gluten-free.
3) The Atkins Diet

The Atkins Diet is a popular low-carb diet that has been around for decades. Low-carb diets are grounded in an idea many call metabolic flexibility, which is your body’s ability to shift from burning carbohydrates to burning fat (and thus promoting fat loss).
As a type of ketogenic diet, Atkins requires you to restrict your carbohydrate intake. By doing so, this diet claims to support healthy and sustainable weight loss as you may be eating fewer calories.
Benefits
There are a variety of Atkins plans designed to help you reach or maintain your target weight. A low-carbohydrate diet has also been shown to reduce average blood sugar levels in those with type 2 diabetes.
Downsides
This diet is focused on weight loss and/or maintenance more than optimizing function. Some researchers have criticized this diet as being unsustainable as a long-term weight loss solution.
Flexibility and Budget
The Atkins diet can require major dietary changes if you are someone who typically enjoys carb-containing foods such as bread, rice, cereals, or pasta. However, with many Atkins-approved recipes available, you’re sure to find options that work within your budget.
Heart-Healthy Diets
There are lots of diets out there that claim to promote cardiovascular health. These diets aim to reduce your risk of heart disease by preventing or reversing hypertension, elevated blood sugar levels, and insulin resistance, which can all have negative effects on your heart health.
Let’s take a look at a few of the most popular heart-healthy diets and the research behind them.
4) The Low FODMAP Diet

The Low FODMAP diet is a short-term elimination diet that was designed to help provide long-term relief for people with IBS or other gut conditions. On this diet, you’ll avoid certain kinds of carbohydrates that can lead to unpleasant GI symptoms.
FODMAPS are types of carbohydrates that may be triggers for irritable bowel syndrome. By removing them from your diet for a short period of time, you may be able to determine which types of foods are leading to uncomfortable symptoms like bloating, diarrhea, or cramping.
Benefits
A low FODMAP diet is generally recommended for people with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO). Some evidence also indicates that it can be effective for small intestinal fungal overgrowth (SIFO) and gut dysbiosis.
This diet may also benefit people with high blood pressure or high blood glucose.
Downsides
The Low FODMAP diet is very restrictive in nature and will require you to learn which foods are high versus low in FODMAPs. As a result, it can be challenging to do on your own.
Consider working with a registered dietitian nutritionist, who can help to determine if FODMAPs could be the source of your symptoms and support you in structuring your meal plan.
Flexibility and Budget
A kind of elimination diet, this diet requires you to avoid all foods high in FODMAPs for two to six weeks. You will then be able to gradually test high FODMAP foods by reintroducing them one at a time.
Many low-FODMAP recipes are available online, so it’s possible to follow this diet based on your personal preferences as long as they qualify as low in FODMAPs. However, given the restrictive nature of this diet, you will need to be mindful when eating out (and bring a cheat sheet with you).
5) The Mediterranean Diet

The Mediterranean Diet is based around the traditional foods that are eaten in countries like Spain, Italy, France and Greece. It’s become a popular diet because of the long life expectancy that’s been found in the populations of these countries.
The Mediterranean Diet is considered to be heart-healthy due to its positive effects on metabolic health factors like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular health. It limits red meat and processed foods and prioritizes whole foods such as:
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Lean proteins like eggs, fish and chicken
- Healthy fats like olive oil and avocado
- Whole grains and legumes
- Dairy products
- Nuts and seeds
Benefits
Research has shown this diet to be highly effective in reducing cholesterol levels and the risk of cardiovascular disease. It is also linked to positive effects on aging and cognitive function. It’s also one of the most simple diets to follow as it does not require you to measure your macronutrient or caloric consumption.
The Mediterranean diet limits your consumption of highly processed and refined foods, added sugars, and trans fats. These are all commonly associated with poor health outcomes when eaten regularly.
Downsides
As this diet is more focused on the types of ingredients you consume, it may not be the most effective option if your primary wellness goal is weight loss. However, it is possible to follow this diet while also being conscious of your caloric intake to reap the benefits while losing weight.
Flexibility and Budget
As we mentioned, this diet is highly customizable, making it easy to follow whether you’re cooking at home or eating at restaurants. Just be sure to focus on eating colorful whole foods, proteins such as fish, tofu, and chicken, and whole grains.
This diet doesn’t have to break the bank, and you can use hacks such as buying frozen fruits and veggies to help reduce the cost of your produce.
6) The Ketogenic Diet

The keto diet is a high-fat, low-carb diet that trains the body to recognize fatty acids, rather than glucose, as its primary source of energy. It was originally developed as a treatment for epilepsy.
On this diet, your body will rely on ketones as its primary fuel source instead of glucose. This is known as a state of ketosis.
This diet is popular among people who want to lose weight, and it is also shown to help with blood sugar regulation.
Benefits
While this diet has been popularized over the last few years among people who want to lose weight, the keto diet has more benefits to it than weight loss.
According to researchers, a keto diet may help:
- Enhance metabolic flexibility
- Reduce insulin levels
- Improve glucose regulation
People who follow the keto diet tend to have very low glycemic variability. Interestingly, low-carb diets such as keto have been shown to be more effective than low-glycemic-index approaches alone for controlling blood sugar.
Downsides
Some research indicates that weight loss from a keto diet stops after one year and that the decrease in fasting glucose levels observed in people with type 2 diabetes may be temporary.
While on the keto diet, you’ll need to monitor your ketone levels to make sure your body doesn’t enter a state known as ketoacidosis. This can be dangerous for your health.
Flexibility and Budget
Carbohydrate intake must be very minimal in order to reach a state of ketosis. The recommended carb intake is 20 to 50 grams per day.
This can make the keto diet difficult to follow compared to other diets as you will have to dramatically increase your consumption of fats and protein. To maintain a healthy intake of produce, opt for low-carb fruits and vegetables.
7) The Paleo Diet

The Paleo Diet is a nutrient-rich diet intended to mimic what some people believe our ancestors ate in the paleolithic era (10,000 years ago). These types of foods include:
- Whole fruits and vegetables
- Grass-fed lean and organ meats
- Free-range eggs, seafood
- Some nuts, seeds, and healthy oils
The scientific basis for this approach is that humans have not evolved genetically to effectively digest gluten, dairy, or lectins (found in legumes). However, there is some controversy among anthropologists over what different paleolithic populations consumed and there can be several different interpretations of what counts as “paleo”.
Benefits
Following some versions of this diet may have potential benefits such as:
- Improvements in glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes
- Improved glucose tolerance in people with ischemic heart disease
- Help with weight management
Similarly to some of the other diets we’ve mentioned, the paleo diet eliminates highly processed foods and added sugars that can have negative health effects. It’s unclear to what degree the observed benefits of this diet for some are due to reductions in these more processed, sugary foods and/or possible carb reductions, or if the other features of this diet contribute just as significantly.
Downsides
The paleo diet can be strict, requiring a lifestyle adjustment to adhere to it for long periods of time. Because it eliminates food groups such as dairy products, legumes, and whole grains, it also may be possible to become deficient in certain micronutrients while on this diet.
Flexibility and Budget
While you can follow a paleo diet without paying for grass-fed or free-range, the optimal way of practicing this diet can be expensive, as these more “natural” items tend to be expensive.
Because of its focus on animal protein sources, it may be more difficult for people already on a plant-based diet or vegan diet to adapt to this eating plan.
8) The Autoimmune Paleo Diet

Also called the Autoimmune Protocol Diet (AIP), this is another type of elimination diet in which you follow a paleo diet while also removing foods known to trigger inflammation and gut dysbiosis. This is thought to lead to improved symptoms of autoimmune diseases.
Here are some of the foods this diet removes:
- Nightshades (tomatoes, eggplant, peppers, potatoes, goji berries, and certain herbs, like ashwagandha)
- Nuts and seeds
- Eggs
- All dairy
- All added sugars
- Coffee and chocolate
- Alcohol
Benefits
Though some small studies have seen improvement in inflammatory markers for those with inflammatory bowel disease, the autoimmune paleo diet has insufficient evidence at this time to support its widespread recommendation for all autoimmune conditions.
Because so many foods are eliminated, the possibility of incidentally eliminating a food or foods you are sensitive to is high. However, there is a question whether or not all of these foods do in fact need to be eliminated for everyone.
Downsides
Following this diet for longer than one year may increase risk of micronutrient deficiencies, which may pose many additional health risks, including possibly negatively impacting the microbiome.
Flexibility and Budget
While this diet may have potential for those with autoimmune conditions, it is even more restrictive than the paleo diet. Consider working with a dietitian to guide you.
Find the right Nutrisense programto turn insight into progress.
Go Beyond Glucose Data with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall wellbeing. But viewing glucose isn't enough. Nutrisense, you’ll be able to learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
One-to-one coaching
Sign up to access insurance-covered video calls to work with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
Monitor and measure what matters
With the Nutrisense CGM Program, you can monitor your glucose with health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitor (CGM)s, and analyze the trends over time with the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.
Find your best fit
Ready to take the first step? Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.

Heather is a Registered and Licensed Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN, LDN), subject matter expert, and technical writer, with a master's degree in nutrition science from Bastyr University. She has a specialty in neuroendocrinology and has been working in the field of nutrition—including nutrition research, education, medical writing, and clinical integrative and functional nutrition—for over 15 years.




