What is Erythritol? Understanding this Sugar Alternative

Key Takeaways
If you are, like many people, looking into reducing your added sugar intake but still want to satisfy your sweet tooth, you have probably explored the world of sugar substitutes. Sweeteners such as stevia, monk fruit, and aspartame have received a lot of publicity in recent years, but what about erythritol?
Erythritol is a naturally occurring sugar alcohol that can be found in a wide variety of common foods, such as grapes, peaches, and cheese. It also contains very few calories, making it a potentially healthier alternative to normal sugar.
In this article, we’ll be taking a deep dive into this lesser known sugar substitute. So, if you’re wondering what the potential benefits and risks erythritol are, keep reading to find out.
What is Erythritol?

Erythritol is a low calorie sugar alcohol that is synthesized from dialdehyde starch. Sugar alcohols, also called polyols, are a type of low-calorie sugar substitute.
Despite their name, however, they don’t contain sugar or alcohol, but rather low-digestible carbohydrates, which aren't fully absorbed or digested by your body. Xylitol, sorbitol, maltitol, and mannitol are examples of other sugar alcohols that are available as sugar substitutes.
Interestingly, erythritol is found naturally in some fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods, but must be synthesized for commercial production. It is only 60-80 percent as sweet as sugar, but contains far fewer calories.
Natural Sources of Erythritol
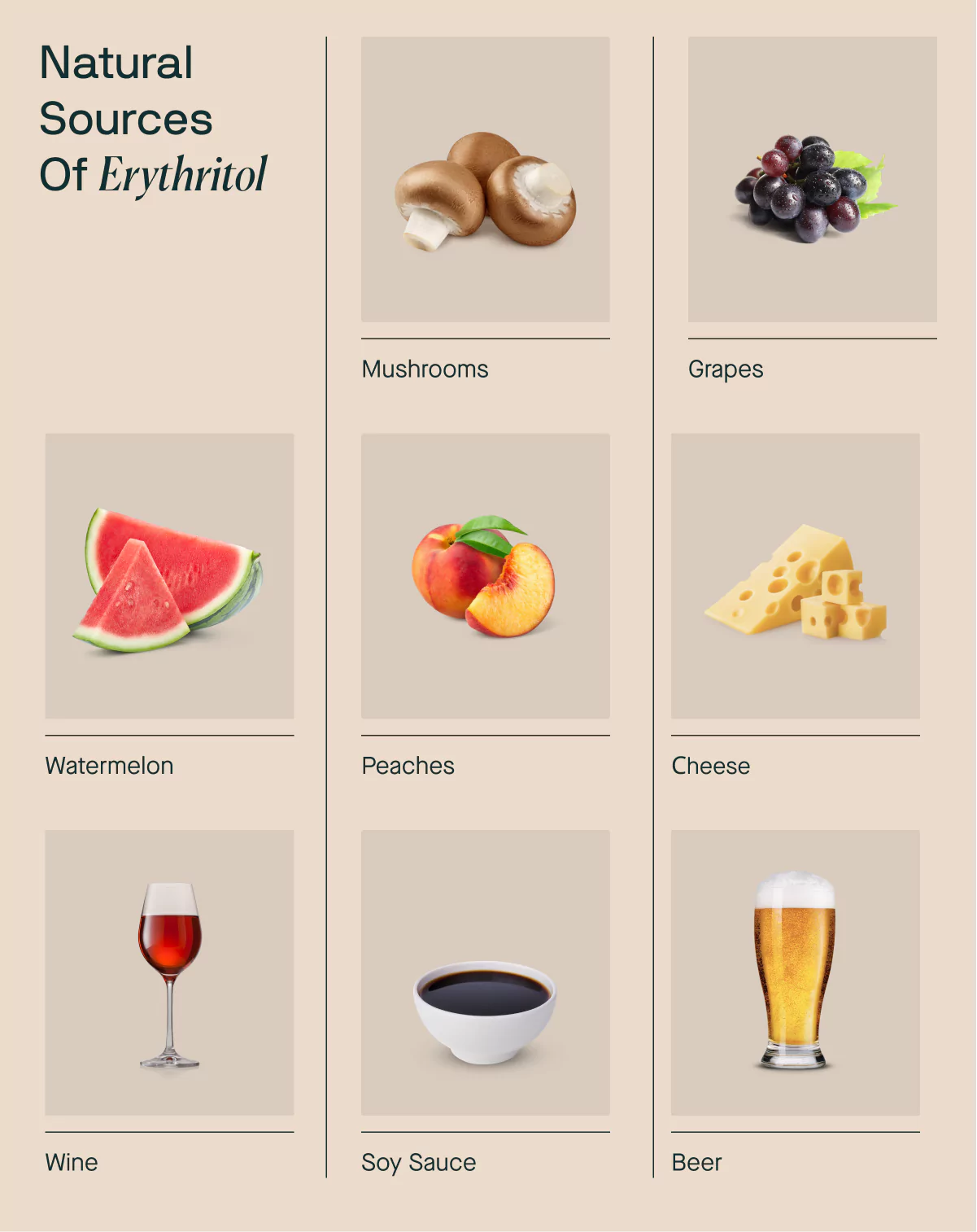
Erythritol naturally occurs in small amounts in several plant foods and food products such as:
- Mushrooms
- Grapes
- Peaches
- Watermelon
- Fermented foods like cheese, soy sauce, wine, and beer
Common Uses for Erythritol
Erythritol is used in a wide variety of foods, cosmetics, and even pharmaceuticals. It is mainly used as a low-calorie sweetener in no-sugar added and reduced-sugar products, like beverages, chewing gum, chocolate, candies, and bakery products.
However, it can also be found in products such as toothpaste, mouthwash, lozenges, medicated chewing gum, and in tablet coatings for medications.
Is Erythritol Safer than Sugar?

As you’re probably aware, a diet high in added sugars has been shown to increase your risk for many health conditions, including:
- Cardiovascular disease
- High blood sugar
- High blood pressure
- Insulin resistance
- Fatty liver disease
- Obesity
- Chronic inflammation
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Type 2 diabetes
Even so, the average American eats more than three times the recommended amount of sugar. Erythritol is generally recognized as safe and is used as an alternative to sugar. It has been shown to havelittle to no effect on blood sugar and insulin levels for most people, making it a better choice for people who have diabetes and hyperglycemia.
Health Benefits of Erythritol
So, are there any benefits to using erythritol as a substitute for sugar? Let’s have a look at three of the potential benefits of this sugar replacement.
1) Low Calorie Content

Calories provide our body with necessary energy, but consuming more than we need can lead to weight gain. Erythritol contains only 1.7 calories per teaspoon, whereas sugar contains 16 calories per teaspoon.
2) Low Glycemic Index
The glycemic index, or GI scale, is a tool originally intended for people with diabetes. As we’ve outlined in our article on the glycemic index of sweeteners, this scale assigns a number to certain foods according to how quickly sugar from food will enter your bloodstream.
Erythritol has a glycemic index of 0, meaning that it will likely not have a negative effect on glucose levels for most people. However, to explore your personal glucose response to erythritol, wearing a CGM can be a helpful tool.
3) Tooth-Friendly

When the bacteria in our mouths metabolizes sugar, it produces an acid that demineralizes the hard tissue of our teeth, leading to cavities and tooth decay.
Erythritol is non-cariogenic, meaning that the bacteria in our mouths does not metabolize it and it doesn’t contribute to tooth decay.
Potential Side Effects of Erythritol
As we’ve discussed, the consumption of erythritol is considered safe by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. However, some people may experience certain adverse reactions to this sugar substitute. Here are some potential side effects of erythritol:
Digestive Issues
For some people, consuming high amounts of sugar alcohols may cause gastrointestinal issues like gas, bloating, and diarrhea.
Allergic Reactions

There have been some reported cases of allergic reactions to erythritol. One woman experienced hives after drinking a beverage containing erythritol.
There have also been some reports of anaphylaxis in children who consumed erythritol. The cause of these allergies is unclear, but they appear to be very rare. If you experience an allergic reaction to erythritol, seek medical attention immediately.
Potential Cardiovascular Risk
A new 2023 study notably linked erythritol to a potential increased risk of heart attack among individuals who were already deemed more likely to experience cardiovascular conditions. As these findings were just released this year, more research is still needed to confirm these findings among larger populations.
However, if you are already at an increased risk of heart disease or stroke, you may want to limit your intake of this sweetener and consult your healthcare provider for guidance.
Comparing Erythritol to Other Sugar Substitutes

Erythritol is just one of many sugar substitutes. Here are some other popular sugar substitutes and how they compare to erythritol.
Stevia
Stevia is a natural sweetener with zero calories derived from a perennial shrub called stevia rebaudiana. The sweetness in stevia is reportedly 200 to 300 times sweeter than table sugar (sucrose).
It is used as a sugar substitute in diet sodas, low-sugar juices, flavored waters, canned fruits, ice cream, yogurt, and baked goods, and is known for its distinct aftertaste.
Stevia and erythritol are both low in calories, have not been shown to impact blood glucose significantly, and are each not linked to tooth decay. In fact, these two sweeteners are both sold together in the form of a sweetener called Truvia.
Neither stevia or erythritol is necessarily healthier than the other—it all comes down to your personal preference.
Allulose

Allulose, also called D-allulose or D-psicose, is a natural sugar that is found in small amounts in plants like wheat, sugar cane, maple syrup, figs, and raisins. It has been shown to possibly have many positive health benefits, including antiobesity, antihyperglycemic, antidiabetes, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and neuroprotective effects. However, these findings are still very preliminary and uncertain to some degree - with more research needed.
Allulose is considered a rare sugar because it’s found in small quantities in nature. Because it’s so rare, and the cost of production is high, it isn’t found in as many products as other natural sugar substitutes.
Like erythritol, allulose has little to no effect on blood sugar and insulin production for most people, is low in calories, and is non-cariogenic. However, it is more expensive to produce than erythritol, so it may not be as readily available.
Splenda
Splenda is a brand of zero-calorie artificial sweetener made from sucralose, the only non-caloric sweetener made from sugar. Splenda also contains dextrose and maltodextrin, which are preservatives and sweeteners made from starch.
Like erythritol, Splenda is not fully absorbed by the body. However, Splenda is an artificial sweetener, a category that has a controversial history when it comes to health benefits and side effects. Many people have reported digestive side effects from sucralose use as well. A 2022 study recently demonstrated that sucralose can alter the gut microbiome and cause dysbiosis in healthy adults.
While much of the research on the safety of artificial sweeteners is contradictory and inconclusive, some studies have shown that artificial sweeteners may increase cravings for sugary foods.
Erythritol may be a healthier choice, as it has fewer potential side effects.
Find the right Nutrisense programto turn insight into progress.
Go Beyond Glucose Data with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall wellbeing. But viewing glucose isn't enough. Nutrisense, you’ll be able to learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
One-to-one coaching
Sign up to access insurance-covered video calls to work with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
Monitor and measure what matters
With the Nutrisense CGM Program, you can monitor your glucose with health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitor (CGM)s, and analyze the trends over time with the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.
Find your best fit
Ready to take the first step? Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.

Heather is a Registered and Licensed Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN, LDN), subject matter expert, and technical writer, with a master's degree in nutrition science from Bastyr University. She has a specialty in neuroendocrinology and has been working in the field of nutrition—including nutrition research, education, medical writing, and clinical integrative and functional nutrition—for over 15 years.




