Why Am I So Bloated: Explained by A Doctor

Key Takeaways
Bloating is an uncomfortable feeling of fullness or swelling caused by trapped gas in your digestive system. Common culprits include certain foods like beans and cruciferous vegetables, food intolerances, constipation, and even swallowing air when you eat. Learning your personal triggers is the first step toward finding relief.
Brief overview:
- Bloating can be caused by dietary choices, such as eating high-fiber foods, dairy, or foods with sugar alcohols like sorbitol and xylitol.
- Medical conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Celiac disease, and Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) can also lead to chronic bloating.
- The Nutrisense program can connect you with a personal dietitian, and video calls are often covered by insurance to help build a personalized plan.
- Simple lifestyle changes like eating slowly, regular exercise, and staying hydrated may help reduce bloating.
Is Bloating Common and What Causes It?
“Why am I so bloated?” is a question you may commonly ask yourself, and it’s a question that plagues many Americans. Unfortunately, bloating is a common discomfort that many of us experience at some point in our lives.
If you’ve experienced this unpleasant feeling and have been in search of a solution, the first step is learning what tends to cause it so you can plan your next move.
So, what exactly causes this sensation of fullness, swelling, and discomfort? Let's look at the science behind bloating and explore the various factors that can cause it.
What Happens During Bloating?
Bloating occurs when there is an abnormal buildup of gas or air in the digestive system, leading to feelings of fullness, discomfort, and abdominal distention. It's a prevalent issue for many, with one study finding that “women were about twice as likely as men to report bloating.”
That Familiar, Frustrating Fullness
You’re getting ready for an afternoon meeting, but the waistband on your go-to work pants feels uncomfortably tight. You had a big salad for lunch, thinking you were making the right choice, yet that familiar sensation of bloating and pressure is back. It’s that confusing feeling of trying to do everything right for your body, only to end up feeling swollen and uncomfortable.
Why Causes Can Be Hard to Pinpoint
What makes bloating a complex topic is that many factors can contribute to it, meaning that determining the exact cause of your bloating can be quite difficult. The processes in the body that lead to bloating are still not completely understood by researchers.
For example, elevated levels of intestinal gas are one factor that can cause bloating and accompanying symptoms. According to studies, the average person has 100 to 200 cubic centimeters of gas within the GI tract at all times .
However, there is no consensus on what counts as an abnormal amount of intestinal gas. As a result, it’s hard for doctors and scientists to measure levels of bloating beyond self-reported symptoms.
Triggers to Consider
The causes of bloating can also stem from various factors - including swallowing too much air, excess water retention, certain dietary choices, underlying conditions, surgery, inability to pass gas, and more.
So, how can you be sure that the discomfort you are experiencing is bloating? The symptoms of bloating can vary from person to person, but some common signs and symptoms include:
Common Symptoms
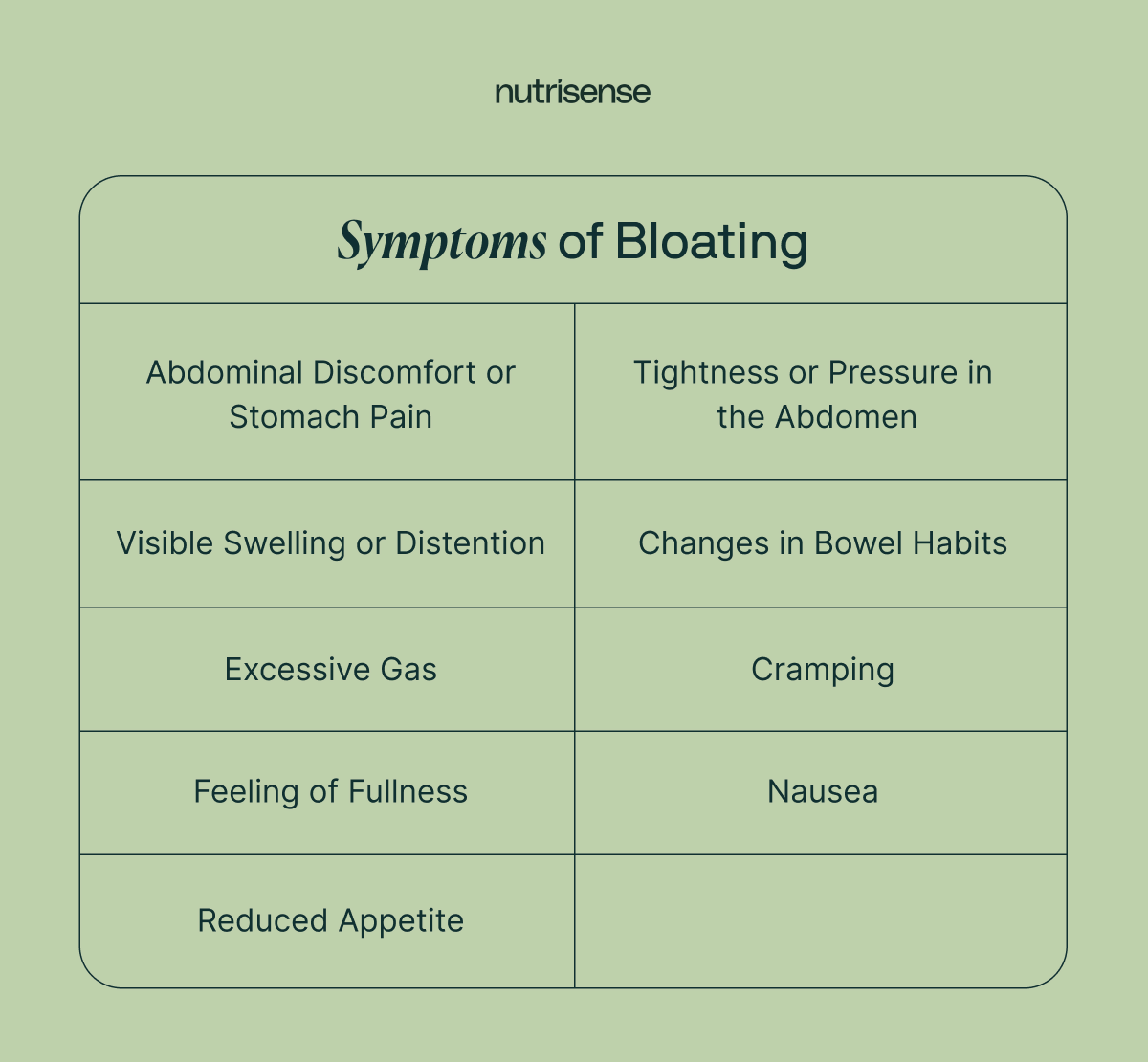
- Abdominal discomfort or stomach pain
- Visible swelling or distention
- Excessive gas
- Feeling of fullness
- Tightness or pressure in the abdomen
- Changes in bowel habits
- Cramping
- Nausea
- Reduced appetite
As you can see, there’s an intricate combination of factors ranging from dietary habits, gut bacteria, digestive processes, and gastrointestinal motility that can influence the occurrence and severity of bloating.
What Causes Bloating?
Let's explore the primary culprits behind bloating symptoms and how they can manifest in your daily life.

Dietary Choices
Your eating habits are a big factor in bloating. A common cause of bloating for some people is the fermentation of undigested carbohydrates by bacteria in the colon. This can result in the production of gases such as hydrogen, methane, and carbon dioxide.
Gas is a normal byproduct of digestion, but excessive gas can cause bloating. This can be caused by eating certain foods, especially high FODMAP foods such as beans, lentils, cabbage, Brussels sprouts, and broccoli.
Other dietary factors, such as overeating, large portion sizes, rapid consumption, chewing gum, and indulgence in carbonated drinks, can all contribute to abdominal discomfort by increasing gas production or causing gastrointestinal irritation.
Food Intolerances
Food allergies or sensitivities, such as gluten or lactose intolerance, can cause bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Food intolerances can trigger bloating for various reasons, including issues with the digestive system, such as dysbiosis.
Underlying Health Conditions
Several underlying medical conditions, such as SIBO/SIFO, IBS, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), or gastroparesis, may exacerbate bloating symptoms, highlighting the importance of seeking medical evaluation for persistent bloating.

- Constipation: This can cause bloating because the stool can become hard and impacted, blocking the passage of gas and stool.
- Irritable bowel syndrome: IBS is a common digestive disorder that can cause bloating or abdominal pain. A low FODMAP diet is often recommended as a temporary elimination diet to help manage these symptoms.
- Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO): SIBO is a condition in which there is an overgrowth of bacteria in the small intestine. This can cause bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
- Celiac disease: This is an autoimmune disorder that can cause damage to the small intestine. This can lead to bloating, diarrhea, and weight loss.
- Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: These conditions are known as inflammatory bowel diseases that can cause bloating and other GI symptoms.
Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly during menstruation, can lead to abdominal bloating. In some studies, ovarian hormonal fluctuations have been linked to bloating, which leads researchers to believe that changes in estrogen and progesterone levels may contribute either directly or indirectly to these symptoms. Check out our article on the best diet for menstruation here.
Other Lifestyle Factors
Certain lifestyle choices, including a sedentary lifestyle, a history of smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption, can aggravate bloating symptoms and impact overall digestive health. In addition to this, factors such as high stress levels have also been linked to increased reports of bloating.
When to See a Doctor About Bloating
See a clinician promptly if bloating appears with red-flag symptoms or feels different than your usual pattern. Bloating is common, but certain signs call for medical care instead of watch-and-wait.
- Blood in your stool or black, tarry stools
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent or worsening abdominal pain
- Fever, persistent vomiting, or inability to keep fluids down
- New or marked swelling in your legs or elsewhere
- Shortness of breath, chest pain, or severe dizziness
- New onset in midlife, or a sudden, severe change after an illness or surgery
If any of these occur, contact your clinician. They may suggest further evaluation, which can include lab work, stool studies, breath testing, or imaging based on your history and exam.
How Can You Avoid Bloating?
Knowing the factors contributing to bloating is the first step towards finding relief. By addressing dietary choices, identifying food intolerances, managing underlying health conditions, considering hormonal influences, and adopting healthier lifestyle habits, individuals can mitigate bloating and enhance their overall well-being.
It's crucial to work closely with a registered dietitian, nutritionist, or healthcare professional to develop personalized strategies for managing and preventing bloating. Here are some practical steps you can take to minimize bloating and discomfort:

- Adopt a Balanced Diet: A well-balanced diet includes lean protein, fruits, and vegetables. An appropriate amount of fiber-rich foods promotes healthy digestion.
- Avoid Overeating: Try to eat until you're comfortably satisfied rather than overly full to avoid overeating, which may also cause a temporary, uncomfortable sensation of bloating.
- Cut Out Carbonated Drinks: Carbonated beverages introduce additional gas into your digestive system, contributing to flatulence and bloating. Consider opting for still water, herbal teas, or other non-carbonated alternatives.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking not only harms your overall health but also contributes to bloating and digestive issues. Kicking the habit can significantly reduce these symptoms.
- Stay Active: A sedentary lifestyle can slow digestion and increase bloating. Staying active, especially after eating, can help keep your digestive system functioning optimally and may reduce bloating.
Supplements
If you’re currently experiencing bloating and seeking relief options, over-the-counter fiber supplements and probiotics may also help relieve certain symptoms. Seeking professional guidance for treatment options can help ensure that dietary and lifestyle adjustments are tailored to your individual needs.
Find the right Nutrisense programto turn insight into progress.
More FAQs about bloating and Nutrisense
Q1. How can I identify my personal bloating triggers using Nutrisense?
A1. Use the Nutrisense app to log meals, ingredients, portion sizes, timing, symptoms, and stress. Pair those logs with 24/7 glucose measured in interstitial fluid from your biosensor to spot patterns after specific foods or meal structures. Try simple side-by-side tests, like changing portion size or cooking method on separate days. Share your notes during a dietitian video call to refine a plan.
Source: Nutrisense App
Q2. Can a Nutrisense dietitian guide a short low FODMAP trial for bloating?
A2. Yes. A registered dietitian can help decide if a short, structured elimination and reintroduction makes sense for you, set up a plan, and keep meals balanced. They will review your logs and glucose trends and help you broaden foods again. Many plans cover video calls. You can check eligibility and book sessions online.
Source: Nutritionist video calls
Q3. How should I track cycle-related bloating and adjust my meals?
A3. To track cycle-related bloating, log cycle days, symptoms, meals, sodium, and carbonation in the app. Compare similar meals at different cycle stages and note any pattern in timing or portion tolerance. Use those notes with your dietitian to adjust meals and hydration during higher symptom days, without restricting entire food groups long term.
Source: The best diet for menstruation
Q4. What if my bloating is persistent or severe?
A4. Nutrisense provides lifestyle guidance only and does not diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent disease. If your bloating is severe, persistent, new, or accompanied by concerning symptoms, contact your healthcare provider. You can still use the app to log meals and symptoms to share with your clinician while you seek evaluation.
Source: Terms of Service
Q5. Can I use Nutrisense if I do not have diabetes but want to explore bloating triggers?
A5. Yes. Many members without diabetes join to log meals and symptoms and view 24/7 glucose patterns measured in interstitial fluid. You can start with the Nutrisense program or choose an app membership if you already have a compatible sensor. Review compatibility and pricing, then sign up online.
Source: Bring Your Own Sensor
Go Beyond Glucose Data with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall wellbeing. But viewing glucose isn't enough. Nutrisense, you’ll be able to learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
One-to-one coaching
Sign up to access insurance-covered video calls to work with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
Monitor and measure what matters
With the Nutrisense CGM Program, you can monitor your glucose with health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitor (CGM)s, and analyze the trends over time with the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.
Find your best fit
Ready to take the first step? Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.
Go Beyond Glucose Data with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall wellbeing. But viewing glucose isn't enough. With Nutrisense, you’ll be able to learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
Meet With a Registered Dietitian
Sign up to access insurance-covered video calls with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
See Your 24/7 Patterns
With the Nutrisense Program, you can monitor your glucose with health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), and analyze the trends over time with the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.
Your Next Step Begins Here
Ready to take the first step? Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.

Victoria began her career in the functional medicine space in 2015. She has extensive experience interpreting labs and supporting weight loss, gut imbalances, and chronic migraines. She received her Bachelor of Science degree in nutrition and dietetics from Missouri State University.


.webp)

