What are the Best Electrolyte Drinks?

Key Takeaways
Proper hydration can significantly impact your health. As we've discussed in past articles, it's helpful for many things—better skin health, good gut health, cognitive function... the list is extensive.
Apart from drinking plenty of plain water, getting enough electrolytes can also play an essential role in keeping you hydrated, especially when you're in warmer environments. However, there are several sports, electrolytes, and hydration drinks out there, and not all of them are created equal. So, how do you know what to pick for rehydration that also offers the best health benefits?
We asked the nutrition experts at Nutrisense to explain electrolytes and why they are important for hydration and health. Plus, Nutrisense dietitian Amanda Donahue, MS, RD, CD, shares her recommendations for healthy electrolyte drink options.
Why Electrolytes Matter For Hydration

Most of your body (about 50 to 70 percent, to be precise) is water! So it’s not surprising you need to stay hydrated to keep it healthy. But hydration isn't just about water content. It also involves balancing the water and minerals in your body, which is where electrolytes come in.
Most people sweat out body fluids and electrolytes during intense exercise and other physical activity. That's why it's essential to hydrate yourself post-workout (especially intense workouts) and replenish your electrolyte levels.
Proper hydration can also be crucial for daily bodily functions, including:
- Body temperature regulation
- Physical performance
- Brain function
- Nerve function
- GI function
- Kidney function
- Cardiovascular health
- Skin health
In fact, severe dehydration may also lead to feelings of low mood, fatigue, and reduced alertness.
The Primary Electrolytes
There are three essential electrolytes our body needs, namely:
- Sodium
- Potassium
- Chloride
Your body also needs calcium and magnesium for multiple functions. Let's examine these, see why they're essential, and how to add them to your diet.
Sodium

Everyone needs a different amount of sodium, so some people with salt sensitivity may do better with slightly lower amounts, while others may need more. The recommended sodium intake for most people is approximately 2300 milligrams per day.
Sodium plays an important role in your nervous system by helping neurons fire properly, which is essential for brain function and muscle movement. After a high-intensity workout, it may help improve athletic performance and avoid muscle cramps. And consuming too much or too little can increase your risk of cardiovascular disease.
The registered dietitians and nutritionists at Nutrisense recommend consuming high-quality salts such as Himalayan pink salt, sea salt, or Redmond salt.
Potassium
Like sodium, potassium helps with fluid balance. It may also be important for heart health, as people who don’t get enough potassium may be at a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Our credentialed nutritionists and dietitians at Nutrisense recommend eating potassium-rich foods like winter squash, potatoes, leafy greens, avocado, seafood, and dairy. Fruits such as watermelon are also excellent sources of potassium.
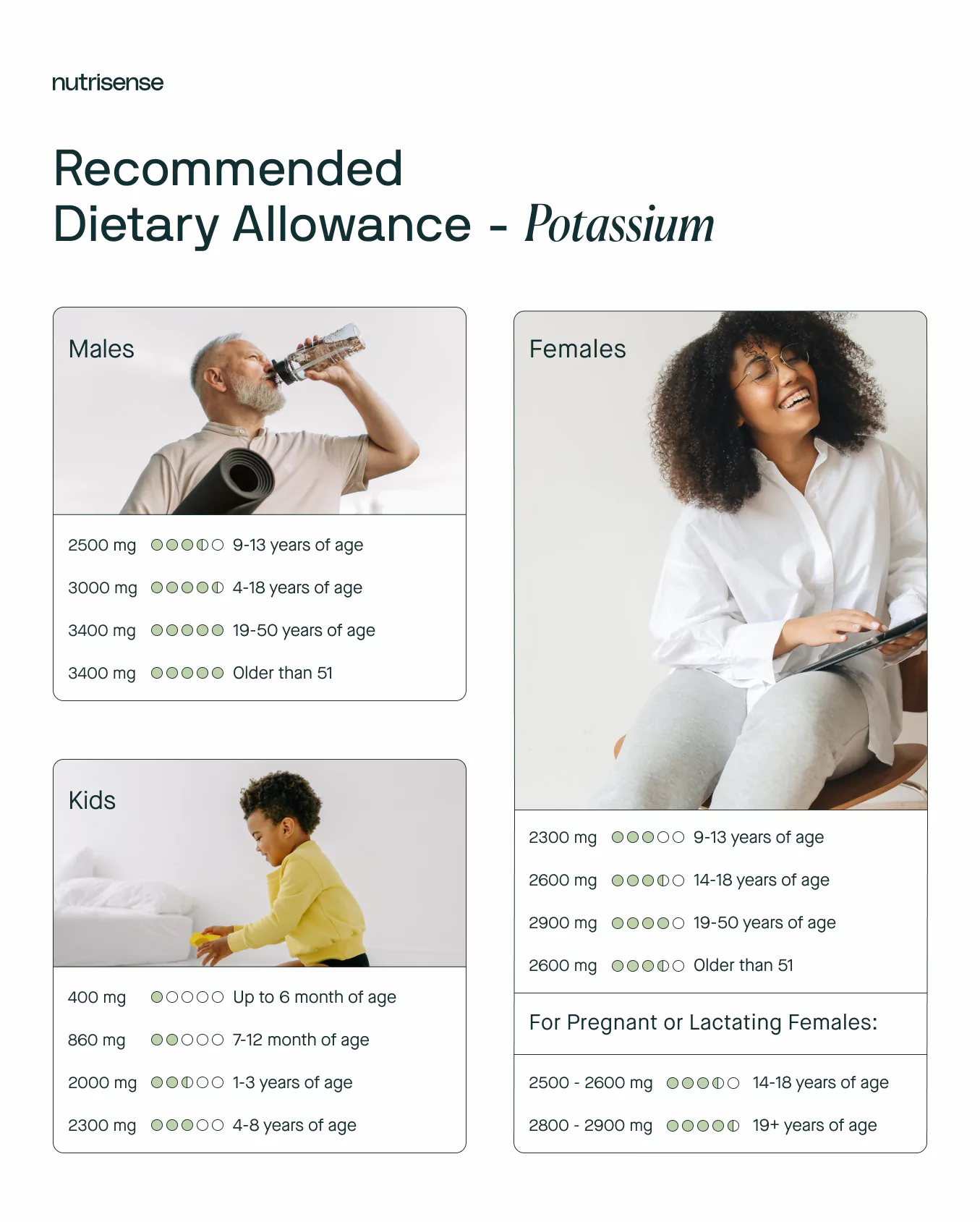
Potassium deficiencies can occur if you cut out or greatly reduce these types of foods from your diet, though certain medical conditions can also lead to a deficiency. The recommended dietary allowance for potassium can vary based on your age and sex:
Chloride
Chloride is very similar in its benefits to sodium (in fact, most foods with sodium will also contain chloride) and potassium. It also produces stomach acid for digestion. It is mostly sourced from table salt (sodium chloride) and helps maintain your body's pH balance.
Chloride deficiency is rare but can occur. Conversely, chloride toxicity, also uncommon, can occur with severe dehydration or certain metabolic conditions. Our experts at Nutrisense recommend keeping your chloride intake balanced to ensure optimal health. The recommended daily chloride intake varies but typically aligns closely with sodium intake recommendations.
Magnesium
You may know magnesium as a muscle relaxant and may have even used it to relax stiff or tired muscles. Some research has also found it beneficial for sleep, feelings of mild anxiety, stress, and PMS symptoms.
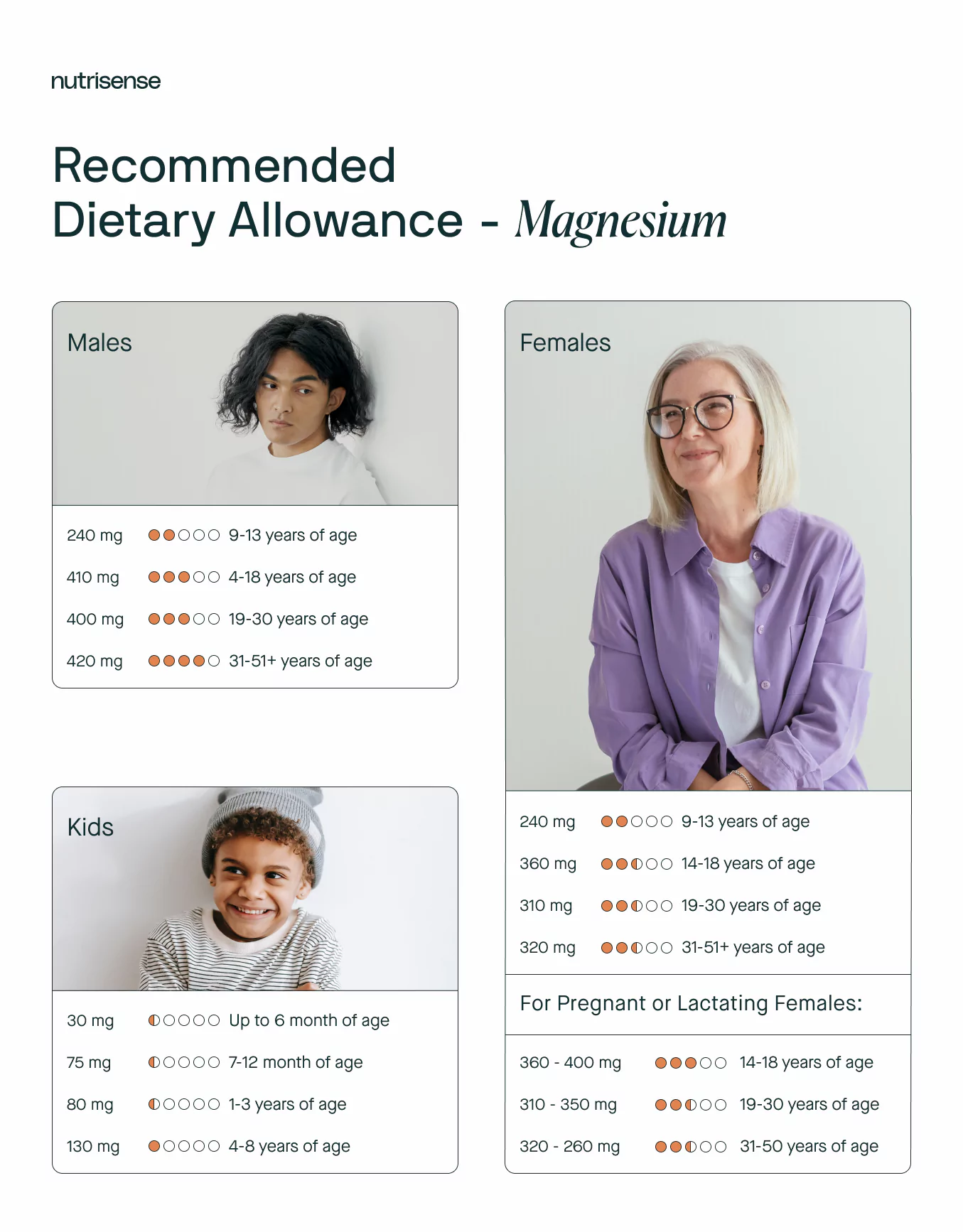
Dark leafy greens, whole grains, and sunflower seeds (and other seeds and nuts to a slightly lesser degree) are the best food sources of magnesium. The recommended dietary allowance for magnesium is:
Calcium
They say milk helps build strong bones for a reason! That's because it contains calcium, which can benefit bone health. However, don’t limit yourself to milk or dairy products.
Other sources of calcium include dark leafy greens, dairy, canned fish with bones, and sesame seeds. Fortified foods are on par with calcium supplements, which may be relatively harder for your body to absorb the higher dose properly.
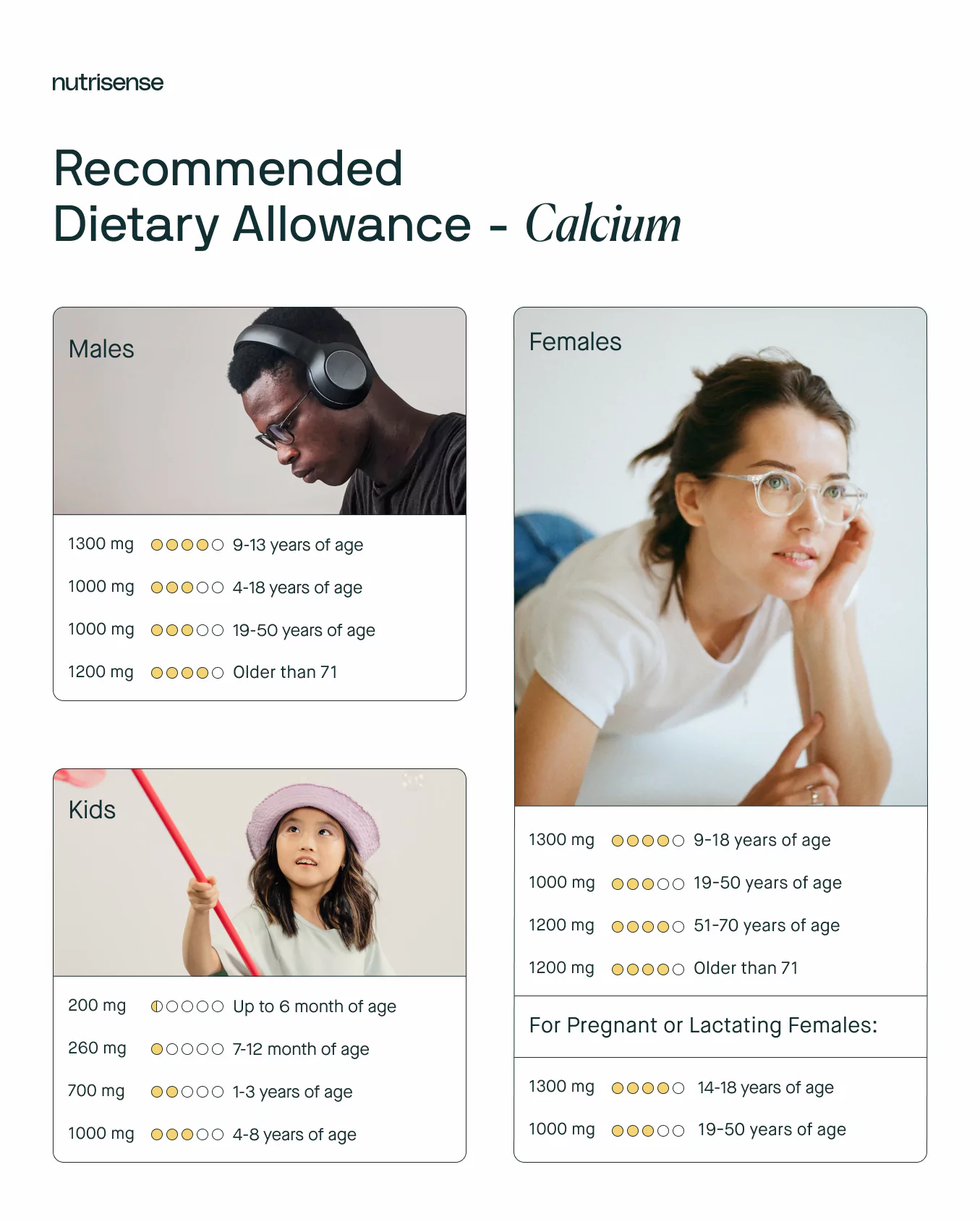
Remember, more calcium isn't always better. Research suggests a link between high-dose calcium supplements and heart disease. The recommended daily allowance for calcium is:
Dietitian-Recommended Electrolyte Drink Options
While there are electrolyte drink options that can be great supplements of these minerals, your best bet is to consume them through food.
Nutrisense dietitian Amanda Donahue, MS, RD, CD, emphasizes,
"Whole foods can be greatly underestimated in their contribution to our electrolyte balance. Given that many whole foods contain considerable amounts of electrolytes and additional nutrients such as protein and other vitamins and minerals, it makes sense to prioritize whole foods as the foundation of our electrolyte balance."
However, for when you need an extra dose of electrolytes, here are four electrolyte drinks that are dietitian-approved!
1) Ultima Replenisher Electrolyte Hydration Mix
This option comes as a powder, and it packs a punch with optimal hydration and no added sugar. Ultima Replenisher products are sweetened with stevia, meaning they're sugar-free.
They offer a variety of flavors, ranging from passion fruit to berry and even citrus. It's paleo, vegan, keto-friendly, caffeine-free…so almost anyone can benefit from it. Simply mix it into your water, fruit juices, and smoothies to add more magnesium, vitamin C, zinc, and potassium to your diet.
This does have lower sodium amounts at 55 milligrams, so keep that in mind if you’re looking for something a little higher.
2) LMNT Keto Electrolyte Powder Packets

This is one of the best electrolyte powders for keto or low-carb diets. LMNT products are also paleo-friendly, gluten-free, and free of sugar, artificial sweeteners, and artificial flavors.
One packet contains 1000 mg of sodium, 200 mg of potassium, and 60 mg of magnesium. To get those electrolytes in, stir in with a beverage or drinking water.
3) Klean Athlete Hydration
Although this option was made for athletes, anyone can benefit from it. Klean products are available in a container and a packet and can be easily dissolved in a glass of water.
If you're buying it in container form, one scoop contains 12.5mg of vitamin C, 35 mg of calcium, 180 mg of sodium, and 70 mg of potassium.
4) Pickleball Cocktail
This orange-flavored option packs a punch for getting that potassium in. One packet contains as much potassium as two bananas!
5) Buoy Electrolyte Drops
These popular electrolyte drops are a convenient way to get a few electrolytes in. The third-party tested product has good ingredients and quality, and it isn’t artificially sweetened. However, it contains some extracts that may add flavor.
Note that its lower sodium content, at around 50 milligrams a serving, makes it less effective as a replacement for electrolytes.
Electrolyte Drinks You May Want to Avoid
You may have noticed that we haven't included some traditional sports drinks like Gatorade, Powerade, and Propel. That’s because commercial sports drinks often have artificial colors and high amounts of added sugar.
For example, a 20-ounce bottle of traditional Gatorade has about 32 grams of sugar. Remember, as registered dietitian Amanda Donahue, MS, RD, CD explains, "These drinks were created with a specific purpose: to hydrate and refuel an athlete performing at high levels (high intensities, longer durations) as they would need the additional sugars for an immediate fuel source."
As for the popular electrolyte powder Liquid I.V.—while this drink mix is made from many natural ingredients, it also contains 11 grams of added sugar per serving! Due to the high sugar content, you may be more likely to have larger glucose spikes.
A few other popular sports drinks you may want to limit when opting for a hydrating boost of electrolytes are Pedialyte Electrolyte Water, Body Armous, DripDrop Electrolyte Powder Packets, and Prime, which can have added sugar or use artificial sweeteners.
Pedialyte's line of electrolyte beverages is sweetened with a mix of sucralose and acesulfame potassium, two artificial sweeteners that may increase the risk of insulin resistance.
Pick Electrolyte Drinks Over Energy Drinks
Many popular energy drinks boast about their vitamin and mineral content but are high in sugar and caffeine while containing minimal beneficial nutrients. And while there may be some mild positive effects in moderate doses, especially for competitive athletes, it’s best to avoid or consume these in moderation.
Like any other caffeinated drink, they are diuretics, so they can actually dehydrate you if you don’t replenish the extra water they make you lose. For those with other health conditions or who have a higher activity level (even endurance athletes), opting for an electrolyte drink is a much better option as it ensures hydration without all the side effects of these sugary drinks. Plus, who wants to deal with the inevitable "crash" after all that sugar?
Do Coconut Water and Mineral Water Hydrate You?
Coconut water has been touted as a natural electrolyte drink, and for good reason. It's a great source of potassium, magnesium, sodium, and calcium — essential minerals that help maintain fluid balance in the body.
Unlike the electrolyte drinks mentioned earlier, coconut water is low in calories and lacks added sugars and artificial flavors, making it a healthier alternative. However, to reap the most benefits, it's important to choose pure coconut water without added sugars or flavors.
Mineral water is another great option for hydration. It naturally contains a variety of minerals, such as calcium, magnesium, potassium, and sodium. These minerals can help replenish electrolytes lost through sweat without any added sugars or artificial ingredients.
Still, mineral waters vary in quality. While some contain a natural balance of minerals, others may have added minerals or flavors. Certain brands also contain higher concentrations of minerals per liter of water.
Are Whole Food Electrolyte Sources Better?
Food sources should ideally be the foundation for electrolyte consumption as much as possible. But why is this? Here’s an explanation from registered dietitian, Heather Davis, MS, RDN, LDN: “Experts promote whole food sources over supplements because they often supply these minerals in their most bioavailable forms as well as in higher amounts compared to electrolyte supplements.
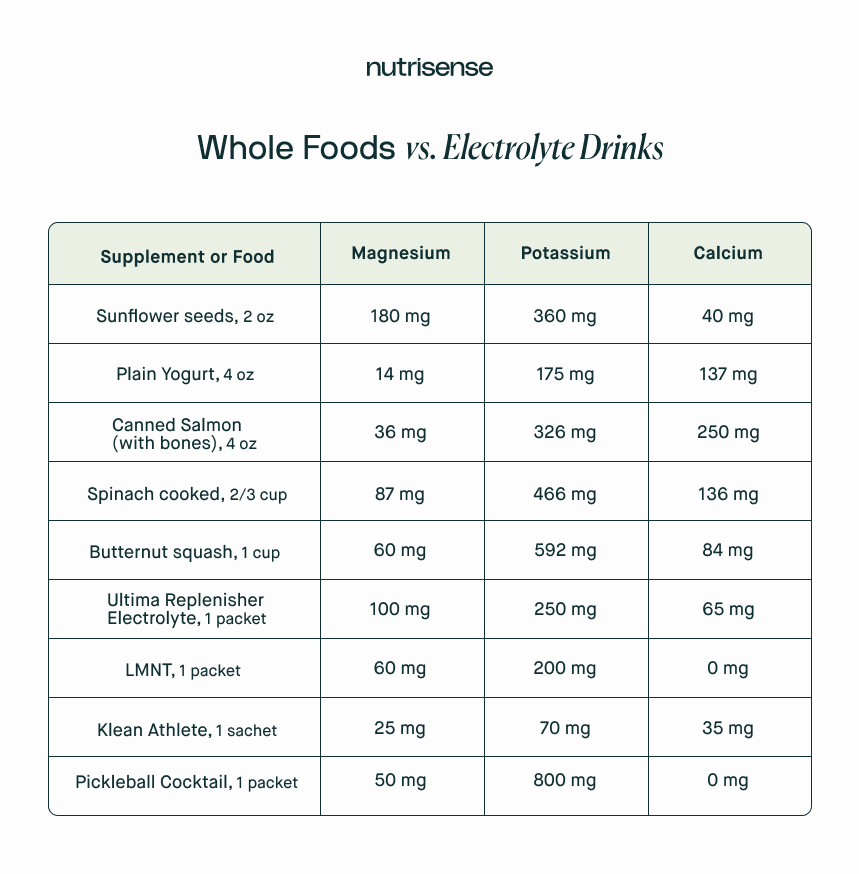
For example, if you eat a well-balanced meal with canned salmon, spinach, and butternut squash, you might get around 183 mg of magnesium, 1300mg of potassium, and nearly 500mg of calcium in a single meal! And we're not even counting the other extra vitamins and antioxidants that you can get from these foods. And if you eat 4 oz of yogurt with 2 oz of sunflower seeds, you might get around 200mg of magnesium, 530 mg of potassium, and 177 mg of calcium in a single sitting.”
If you're looking for an extra boost of electrolytes, electrolyte drinks can be a quick, easy way to add extra minerals to your day. However, as we've seen above, there are many easy ways to add extra electrolytes into your diet without the help of a drink or supplement. Remember to read the ingredient list to note the sodium content, minerals, and vitamins in a single serving before you choose.
Find the right Nutrisense programto turn insight into progress.
Track Your Blood Glucose Responses to Various Electrolyte Drinks with Nutrisense
Do you drink water or electrolyte drinks when you feel thirsty? Do you need an energy drink after a hard workout or athletic event? How do these decisions affect your blood glucose levels?
Consider speaking with a registered dietitian or nutritionist (someone with specialties in sports nutrition would be even better!) to find out what electrolytes your body needs, whether you can get them from the drinks you pick, and how they match your health goals. You can also use a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) to track trends in your blood glucose levels and see how different beverages and foods impact them.
Ready to take charge of your health and hydration? Try our quiz to see what plan is the perfect fit for your needs.
Go Beyond Glucose Data with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall wellbeing. But viewing glucose isn't enough. Nutrisense, you’ll be able to learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
One-to-one coaching
Sign up to access insurance-covered video calls to work with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
Monitor and measure what matters
With the Nutrisense CGM Program, you can monitor your glucose with health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitor (CGM)s, and analyze the trends over time with the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.
Find your best fit
Ready to take the first step? Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.

Heather is a Registered and Licensed Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN, LDN), subject matter expert, and technical writer, with a master's degree in nutrition science from Bastyr University. She has a specialty in neuroendocrinology and has been working in the field of nutrition—including nutrition research, education, medical writing, and clinical integrative and functional nutrition—for over 15 years.




