Does Eating Too Much Sugar Affect Your Skin?

Key Takeaways
Did you know that the skin is your body's largest organ? It's part of something known as the integumentary system (or, in simpler terms, your body's outer layer) and includes hair, nails, sweat, and oil glands. Healthy skin can work to protect your body from various factors, including bacteria and chemicals.
Many lifestyle and dietary factors can influence skin health. Excessive UV light exposure, dehydration, what you eat and drink (like alcohol use, for example), and cigarette use can all cause skin damage and premature aging.
So, it’s no surprise that proper nutrition is one way to focus proactively on skincare and reduce your risk of certain skin conditions. On the other hand, poor nutrition can lead to flare-ups of certain skin conditions, such as dermatitis and skin aging. One of the biggest offenders here is sugary foods!
As tasty as sweet treats may be, including too much in your diet can cause many issues apart from bad skin: fatigue, imbalanced blood sugar levels, and so on. Today, let’s focus on learning more about the role some sources of sugar (especially added and processed sugars) play in skin health.
Glucose and Skin Health

For those at risk of diabetes or already living with it, how your skin looks and feels can be one of the prominent signs that your blood sugar levels are too high. Skin patches, hardened skin, blisters, or bumps can all be indicators of diabetes and other chronic diseases.
High glucose levels have also been linked to other skin conditions, such as acne breakouts, wrinkles, and premature signs of aging. They can even increase symptoms of inflammation and oxidative stress.
Luckily, a few changes to your diet can help you prevent the adverse side effects of excessive sugar intake, including weight gain and the risk of obesity. Reducing your consumption of added sugars may also help you protect your skin and prevent other conditions caused by excess sugar consumption.
Does Sugar Make Your Skin Worse?
Yes, excess sugar can adversely affect your skin. Some of the effects of sugar can be worsening conditions like psoriasis and rosacea, premature wrinkles, and acne. Here’s a quick breakdown:
Sugar Can Lead to Fine Lines and Wrinkles
One of the effects of sugar on your skin is that it may increase your risk of getting fine lines and wrinkles earlier than you typically would. Of course, many factors can contribute to wrinkles as your skin ages, and while they’re inevitable (and there’s nothing wrong with aging naturally!), taking preventative measures can reduce your chances of developing them prematurely.
Glycation, which can lead to wrinkles, is caused by too much glucose in the skin's fibers, which develops advanced glycation end products (AGEs). These effects cause collagen to become less elastic, leading to age-related, droopy skin. Less elastin production also causes the skin to become thinner and more fragile.
People who consume excess sugar daily may see more AGEs forming in the skin and develop more wrinkles. Unfortunately, the AGEs that result from excessive sugar consumption go beyond wrinkles.
Studies have also linked them to pathologies related to diabetes, cardiovascular conditions like heart disease and stroke, kidney disease, and liver disease. The frequent blood sugar spikes resulting from excessive intake of sugar also cause insulin levels to increase. Plus, they can also put you at a higher risk of developing insulin resistance, brain fog, and other mental health issues.
Sugar Can Cause Acne Breakouts
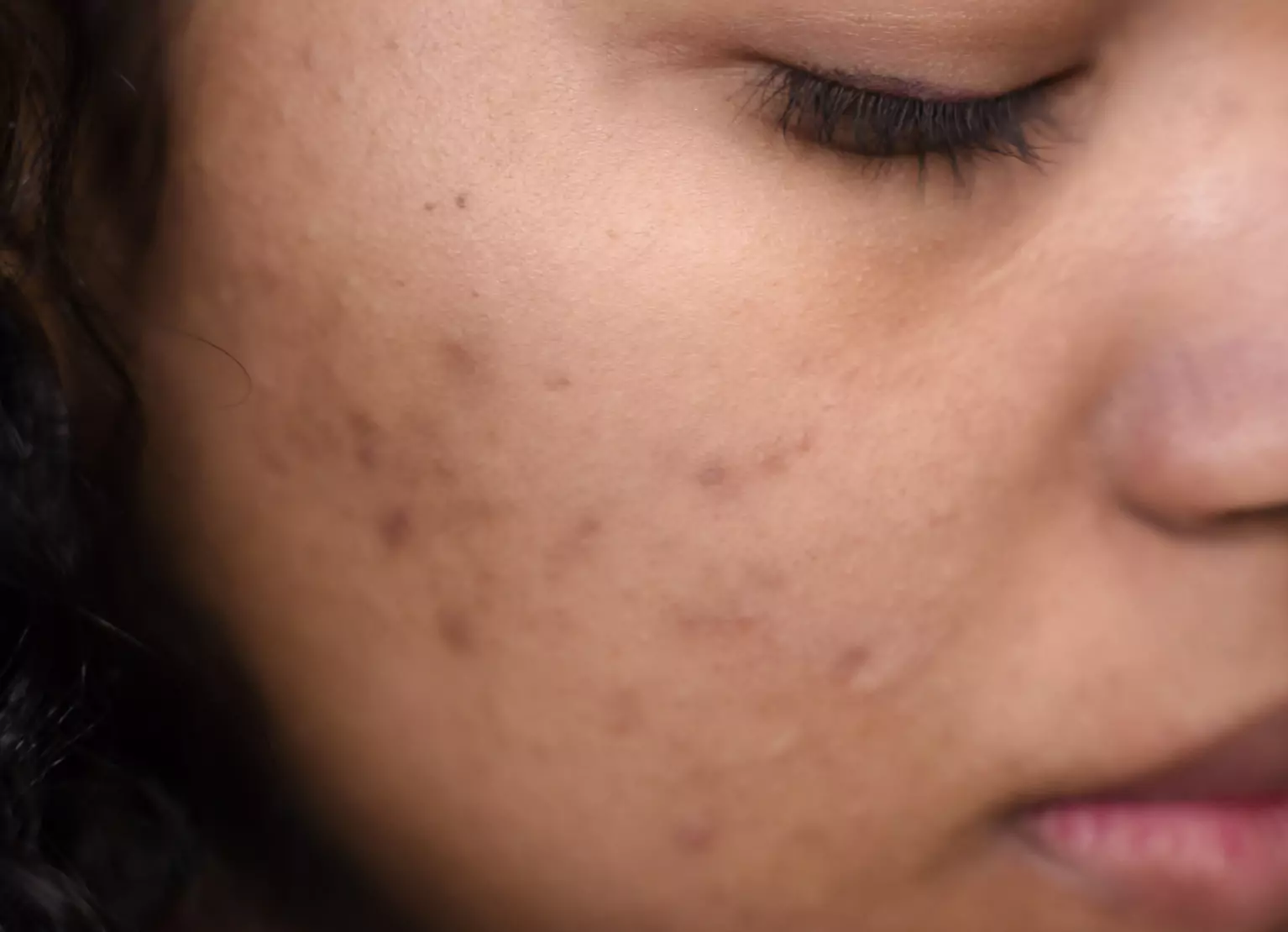
Most scientists and dermatologists agree that diet, pollution, stress, sleep quality, and other external environmental factors can impact the development of acne. While research is still ongoing, a correlation has also been found between diets with a high glycemic load and the presence of acne. Other studies have also found a link between Western diets containing dairy and high glycemic index content, which affects hormone levels and may trigger acne. However, more research on the effects of dairy on acne is still needed.
Dietary patterns, such as those containing excessive sugar, are just one factor associated with higher sebum production, which can lead to increased acne. So, if you're someone who experiences acne, reducing high-glycemic food intake might be one way you can prevent breakouts.
Sugar May Cause Inflammation
Inflammation is usually a healthy response by our body to fight viruses or other infections. But when it becomes chronic, it can negatively affect your body.
When it comes to skin health, some research has shown that eating high-sugar foods can trigger an inflammatory response that can exacerbate skin conditions related to inflammation, such as psoriasis and eczema.
Reducing sugar intake may help control symptoms related to inflammation for those with skin conditions. Chronic inflammation caused or worsened by dietary sugar damages the skin and can increase the risk of developing diabetes. It's also a key risk factor in many other health conditions, such as dementia, depression, and cardiovascular disease.
Sugar Stimulates Oil Production in the Skin

Sebum, an oil produced by your body's sebaceous glands, naturally coats the skin to keep it moisturized and protected. Some studies have indicated that excessive sugar consumption may be associated with high sebum production, which causes oily skin.
In addition to excess oil, sebum has also been found to increase the risk of acne in some individuals, indicating that reducing sugar may also indirectly reduce acne.
More research is still needed to confirm the connection between sugar and other dietary factors that may affect oily skin.
Tips to Help Reduce Your Sugar Intake
Will cutting out sugar help your skin? Maybe. But reducing your sugar intake doesn't mean you have to cut all sugar out of your diet. Instead, educating yourself about where added sugars are hiding and trying to swap those foods out for healthier alternatives from time to time can be a great place to start. Not only will your skin thank you, but you can also reduce your risk of many other health conditions linked to sugar intake.
Here are some tips to consider if you want to consume less sugar:
Eat Fewer Processed Foods and More Whole Foods
Because sugar is commonly found in prepackaged and processed foods, drinks, and sauces, sticking to a whole-food-focused diet is one of the best ways to control sugar consumption.
Many ultra-processed foods are loaded with artificial sugars, flavorings, and other sweeteners, providing little nutritional value. So, while you shouldn’t eliminate all natural sugars in your diet, some examples of foods you may consider reducing your consumption include sugar-sweetened beverages, candy, ice cream, and frozen meals.
Cutting all processed foods from your diet isn't possible; these foods can be fine in moderation. Most dietitians recommend focusing on high-quality protein, fruits and vegetables, and whole grains and limiting consumption of refined carbohydrates, refined oils, added sugars, and trans fats.
Stay Away from Sugary Drinks

Sugary drinks are notorious for their addictive nature and can be challenging to cut out. But most soda, and even some store-bought fruit juices, can be high in calories and provide little nutritional value.
Some studies have shown that frequent consumption of sweetened drinks has often been associated with weight gain, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease. Recently, a strong link between the consumption of sugary beverages and certain types of cancer was also discovered, demonstrating that eliminating these drinks from your diet can positively impact things besides skin quality.
Limiting sugary drinks is best because it is so easy to over-consume them as much as possible. Medical professionals recommend limiting your consumption to less than four ounces per day.
Find the right Nutrisense programto turn insight into progress.
Go Beyond Glucose Data with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall wellbeing. But viewing glucose isn't enough. Nutrisense, you’ll be able to learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
One-to-one coaching
Sign up to access insurance-covered video calls to work with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
Monitor and measure what matters
With the Nutrisense CGM Program, you can monitor your glucose with health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitor (CGM)s, and analyze the trends over time with the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.
Find your best fit
Ready to take the first step? Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.

Katie is a dietitian at Nutrisense. With over 11 years of experience as a dietitian in many areas of nutrition, Katie has worked as a clinical dietitian within a hospital, as well as in the fields of diabetes, sports and performance nutrition, recovery from addiction, and general wellness. She’s also an athlete and has run 8 marathons, including the Boston Marathon.




