Is MiO Bad for You? Ingredients, Side Effects, and Alternatives

Key Takeaways
- Is MiO Bad for You? It depends. While recognized as safe by the FDA, MiO contains artificial sweeteners and dyes that may disrupt the gut microbiome or trigger sensitivities in some individuals.
- Does MiO Raise Glucose? Generally, no. However, some research suggests the "sweet taste" of sucralose can trigger an insulin response (cephalic phase) in certain people
- Best Alternatives: Natural electrolytes and fruit-infused water are superior for metabolic health.
- Is MiO Bad for You? It depends. While recognized as safe by the FDA, MiO contains artificial sweeteners and dyes that may disrupt the gut microbiome or trigger sensitivities in some individuals.
- Does MiO Raise Glucose? Generally, no. However, some research suggests the "sweet taste" of sucralose can trigger an insulin response (cephalic phase) in certain people
- Best Alternatives: Natural electrolytes and fruit-infused water are superior for metabolic health.
Staying hydrated is vital for cognitive health and metabolic function. However, busy lifestyles often lead us to convenient, flavored options.
If you struggle with drinking enough water, you may have wondered if MiO water enhancers can help. Similarly to brands like Crystal Light and Sweet Leaf, MiO is a liquid water enhancer that is designed to help you customize plain water with different flavors.
But is this flavored water enhancer good for you? Read on to learn more about MiO, its ingredients, and how it may affect your health.
What is MiO?
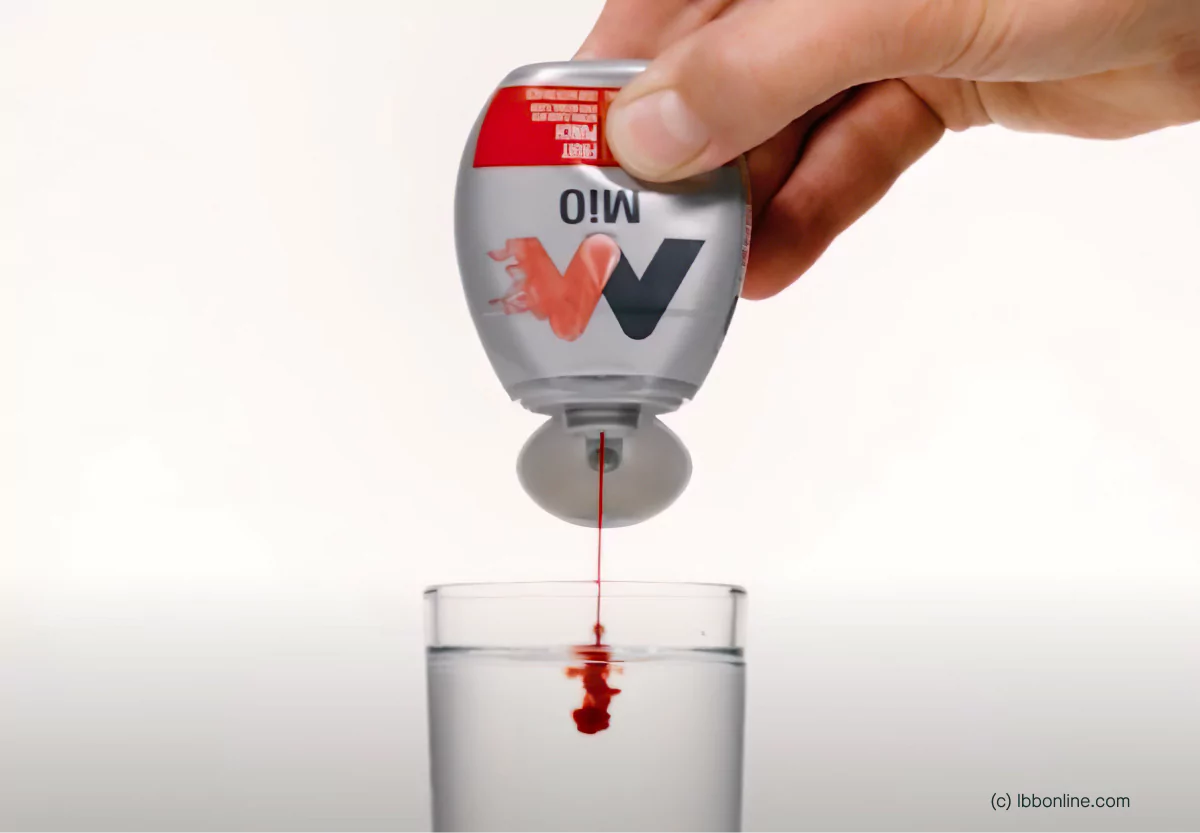

MiO is a sugar and calorie free liquid water enhancer. Each MiO product is available in a variety of flavors and sweetened with the artificial sweeteners sucralose and acesulfame potassium.
MiO sells four different products:
- MiO Original: The standard liquid water enhancer used to flavor plain water.
- MiO Energy: which contains about 60 milligrams of caffeine per half serving (roughly equal to a shot of espresso) plus B vitamins
- MiO Vitamins: Fortified with Vitamins B3, B6, and B12 (10% DV).
- MiO Electrolytes: Positioned as a low-calorie sports drink alternative, containing 75mg of sodium and 35mg of potassium per serving.
Some flavors of MiO Vitamins are naturally sweetened with stevia leaf extract. As a result, they’re sugar free and have zero calories, and have been marketed as a healthy replacement for sugary drinks such as sodas and juices.
How is MiO Used?
MiO’s different products are designed to add natural flavor, vitamins, and/or caffeine to your water. You can easily add MiO to a glass of water, sparkling water, or a water bottle to help boost your daily hydration.
MiO is sold in a 1.62 fluid-ounce bottle. Because it’s a concentrated liquid, it’s meant to be diluted with at least eight ounces of water. MiO flavors and products can be mixed together, but they are not designed to be mixed with alcohol.
MiO doesn’t require refrigeration, but it should be used within 30 days of opening. If you are pregnant or breastfeeding, talk to your doctor before drinking MiO.
Is MiO Bad for You?

While MiO claims to be a healthy water enhancer, there are some potential side effects and health concerns associated with some of the ingredients found in MiO products. These include artificial sweeteners, synthetic dyes, and preservatives.
Let’s take a look at what potential health effects these ingredients can have on your overall health.
Artificial Sweeteners
Artificial sweeteners are synthetic sugar substitutes. They have virtually no calories and are about 200-600 times sweeter than sugar. They are regulated by the United States Food and Drug Administration as food additives.
Artificial sweeteners have been shown to have some negative side effects, although this is the subject of some debate. One 2010 study found that the sweet taste of artificial sweeteners might increase sugar cravings and encourage sugar dependence.
This might explain why other studies have found that people who drink beverages sweetened with artificial sweeteners may actually gain weight. Other studies, however, have found conflicting results, meaning that more research in this area is still needed.
Some artificial sweeteners have come under scrutiny for potential altering the gut microbiome in ways that may increase risk of certain metabolic diseases.
Currently, six artificial sweeteners, also called high-intensity sweeteners, are approved by the FDA. These include:
- Saccharin
- Aspartame
- Acesulfame potassium (Ace-K)
- Sucralose
- Neotame
- Advantame
Sucralose

Sucralose is one of the artificial sweeteners found in MiO. It is currently the only non-caloric sweetener made from sugar. It is made by replacing three hydroxyl groups in sugar with three chlorine atoms.
Though some studies show that sucralose has no effect on blood sugar or insulin production, other research shows that it may decrease insulin sensitivity and affect blood sugar. There is also evidence to suggest that sucralose may have a negative effect on the bacteria in your gut microbiome.
Studies done in animals have suggested that sucralose’s interaction with gut bacteria may play a role in chronic inflammation, but more research is needed to establish a link in humans.
Ace-K (Acesulfame Potassium)
Acesulfame Potassium, or Ace-K, is an artificial sweetener that is about 200 times sweeter than sugar. Though this sweetener is approved by the FDA, organizations like the Center for Science in the Public Interest urge people to avoid Ace-K until further testing is carried out.
This is because during the initial safety testing, rats used in animal tests were poorly attended, and randomization for the test subjects was also not properly carried out.
One 2017 study on mice also found that Ace-K may have a negative effect on the healthy bacteria in the gut microbiome of mice, which led to weight gain and disruptions in energy metabolism. However, more research and human studies are needed to establish a link.
Artificial Dyes
MiO contains artificial food dyes, also called color additives. Some color additives used in MiO include Yellow 5, Yellow 6, Red 40, and Blue 1. Even though the FDA has approved these dyes for use in food products, there is some concern about the potential health risks they may cause.
For example, some studies have suggested that artificial colorings may contribute to hyperactivity in children, particularly Yellow 5 and Red 40, which are among the most widely used color additives in the U.S.
Other studies have found that Yellow 5 could be associated with trouble sleeping and increased irritability in children, but further study is needed. All of the artificial dyes used in MiO may also cause hypersensitive or allergic reactions in some people.
Preservatives
MiO products contain propylene glycol, which is a thick, odorless and colorless liquid that is used as a preservative. Propylene glycol absorbs extra water and maintains moisture in many products.
While it’s generally considered safe, high and repeated exposure, particularly to skin, may have negative effects on the central nervous system and heart. Ingestion of foods with propylene glycol have also been shown to cause contact dermatitis, which is an inflammation of the skin.
MiO also contains potassium sorbate, which is a chemical additive that is synthetically produced for use as a preservative. Research has found evidence to suggest this additive may lead to cytotoxic and genotoxic effects, which can have a number of side effects on your health.
What Else is in MiO?

B Vitamins
MiO Energy and MiO Vitamins contain Vitamins B3, B6, and B12. B Vitamins are essential nutrients that help our bodies function properly.
Vitamin B3, also called niacin, helps you obtain energy from food you eat. It’s important for brain function, communication between cells, and maintaining the antioxidant function of your cells.
Vitamin B6 performs many functions in the body, including cognitive development, immune function, and metabolism. Some studies suggest that vitamin B6 in adequate amounts may play a role in preventing some types of cancer, but more research is needed to confirm these findings.
Vitamin B12 is a nutrient that helps keep your blood and nerve cells healthy, helps energy levels, and helps make DNA. Vitamin B12 deficiency can make you feel tired and weak, cause depression, cause balance and memory problems, and damage the nervous system.
It’s important to note that adequate intake of B vitamins can ideally be achieved through eating foods rich in these vitamins, such as protein-rich foods. Research shows that consuming additional supplemental B vitamins beyond what is needed for adequacy offers no additional health benefit and excess intake may cause more harm than good.
Electrolytes
Some MiO products, like MiO Sport, contain the electrolytes potassium and sodium. Electrolytes have a natural positive or negative charge when dissolved in water. Your body uses these charges to transport chemicals in and out of cells and help your cells maintain the right balance of fluid.
Many foods contain electrolyte minerals in adequate amounts to meet your electrolyte needs, as long as you’re eating plenty of nutrient-dense whole foods.
Stevia
Unlike Ace-K and sucralose, stevia is considered a natural sweetener. Stevia is 200-300 sweeter than sugar, and its sweetness comes from compounds called stevioside and rebaudioside A and C.
Because it isn’t fully absorbed by the body, stevia doesn’t have a negative effect on blood sugar control, insulin production, or fasting blood sugar levels for most people. It is non-cariogenic, meaning it won’t cause tooth decay.
Currently, stevia is only used to sweeten certain flavors of MiO Vitamins. Other MiO alternatives may rely on other sweeteners.
Does MiO Affect Blood Sugar?
Studies show that sucralose, which is used in MiO, is partially metabolized by the body and may affect blood sugar level. The sweet taste receptors in your gastrointestinal tract may increase insulin production in response to sucralose, increasing the risk for potential blood sugar spikes.
This research also suggests that drinking high-intensity sweetened beverages may impair the release of glucagon-like peptide-1, or GLP-1. GLP-1 is a hormone that helps regulate insulin production, delays gastric emptying, and increases satiety. Impaired GLP-1 secretion can lead to weight gain and increased blood sugar.
The sweetener used in the MiO product of choice may impact this, however, since research shows that stevia does not tend to affect blood sugar. If you are opting to use MiO, the naturally sweetened varieties of MiO may be your best bet when it comes to avoiding blood sugar spikes.
Does MiO Have Any Health Benefits?

If you have trouble drinking enough water because you prefer sweetened beverages, MiO water enhancers may help you increase your water intake.
However, MiO contains artificial sweeteners, dyes, and preservatives that may have side effects. High-intensity sweeteners present in MiO have also been shown to increase sugar cravings and sugar dependence in the long run.
MiO is considered safe to use by the FDA and its ingredients may have some health benefits. Still, you may want to consider your particular diet and health needs when deciding if MiO could be a healthy addition to your lifestyle. Consider consulting with an expert, like a credentialed nutritionist if you want to add MiO to your diet.
Healthy Alternatives to MiO (That Won't Spike Glucose)
If you are looking for a MiO alternative that avoids artificial dyes and preservatives while supporting metabolic health, consider these options:
1. Natural Electrolyte Powders
Look for electrolyte brands that use Stevia or Monk Fruit rather than Sucralose or Ace-K. These provide hydration support without the potential microbiome disruption associated with artificial sweeteners.
2. Fruit-Infused Water (Spa Water)
Adding whole ingredients adds micronutrients without the chemical additives. Good options include:
- Lemon or Lime: Adds citrate which may support kidney health.
- Cucumber & Mint: Refreshing without added sugars.
- Muddled Berries: Provides a small amount of polyphenols.
These natural infusions are less likely to trigger the sugar cravings sometimes associated with hyper-sweet artificial enhancers.
Find the right Nutrisense programto turn insight into progress.
Go Beyond Glucose Data with Nutrisense
Your glucose can significantly impact how your body feels and functions. That’s why stable levels are an important factor in supporting overall wellbeing. But viewing glucose isn't enough. Nutrisense, you’ll be able to learn how to use your body's data to make informed lifestyle choices that support healthy living.
One-to-one coaching
Sign up to access insurance-covered video calls to work with a glucose expert: a personal registered dietitian or certified nutritionist who will help tailor your lifestyle and diet to your goals.
Monitor and measure what matters
With the Nutrisense CGM Program, you can monitor your glucose with health tech like glucose biosensors and continuous glucose monitor (CGM)s, and analyze the trends over time with the Nutrisense App. This will help you make the most informed choices about the foods you consume and their impact on your health.
Find your best fit
Ready to take the first step? Start with our quiz to find the right Nutrisense program to help you take control.
Frequently Asked Questions About MiO
Is MiO bad for your kidneys?
There is no direct clinical evidence that MiO causes kidney damage in healthy individuals when consumed in moderation. However, MiO contains artificial sweeteners and dyes. Individuals with specific kidney conditions (like CKD) who need to monitor potassium or sodium intake should consult their healthcare provider, especially regarding MiO Electrolytes.
Does MiO break a fast?
Technically, MiO contains negligible calories, so it does not break a fast in terms of caloric load. However, for those fasting for metabolic health, the sweet taste of sucralose may trigger a cephalic phase insulin response in some individuals, potentially pausing fat oxidation. A CGM can help you verify your personal response.
Does MiO have caffeine?
MiO Energy contains caffeine (60mg per serving), while MiO Original, MiO Vitamins, and MiO Electrolytes are typically caffeine-free. Always check the label if you are sensitive to stimulants.

Heather is a Registered and Licensed Dietitian Nutritionist (RDN, LDN), subject matter expert, and technical writer, with a master's degree in nutrition science from Bastyr University. She has a specialty in neuroendocrinology and has been working in the field of nutrition—including nutrition research, education, medical writing, and clinical integrative and functional nutrition—for over 15 years.




